Page 323 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 323
8.2 O/F LIGAND EXCHANGES 303
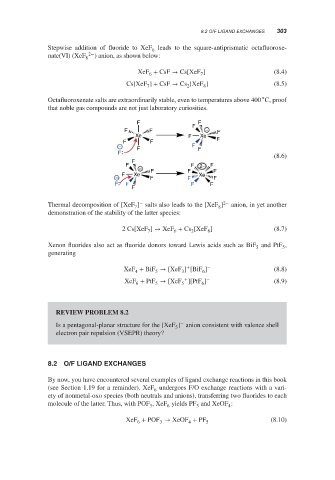
Stepwise addition of fluoride to XeF leads to the square-antiprismatic octafluoroxe-
6
nate(VI) (XeF 8 2− ) anion, as shown below:
XeF + CsF → Cs[XeF ] (8.4)
6
7
Cs[XeF ]+ CsF → Cs [XeF ] (8.5)
8
2
7
∘
Octafluoroxenate salts are extraordinarily stable, even to temperatures above 400 C, proof
that noble gas compounds are not just laboratory curiosities.
F F
F
F F − F
Xe F Xe
F F F
− F
F F
F
(8.6)
F
F F 2− F
− F F F
− F Xe F F Xe F
F F F F
F
−
Thermal decomposition of [XeF ] salts also leads to the [XeF ] 2− anion, in yet another
8
7
demonstration of the stability of the latter species:
2Cs[XeF ] → XeF + Cs [XeF ] (8.7)
7 6 2 8
Xenon fluorides also act as fluoride donors toward Lewis acids such as BiF and PtF ,
5
5
generating
+
XeF + BiF → [XeF ] [BiF ] − (8.8)
5
3
6
4
+
XeF + PtF → [XeF ][PtF ] − (8.9)
6
5
5
6
REVIEW PROBLEM 8.2
−
Is a pentagonal-planar structure for the [XeF ] anion consistent with valence shell
5
electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory?
8.2 O/F LIGAND EXCHANGES
By now, you have encountered several examples of ligand exchange reactions in this book
(see Section 1.19 for a reminder). XeF undergoes F/O exchange reactions with a vari-
6
ety of nonmetal-oxo species (both neutrals and anions), transferring two fluorides to each
molecule of the latter. Thus, with POF ,XeF yields PF and XeOF :
3 6 5 4
XeF + POF → XeOF + PF 5 (8.10)
3
4
6