Page 325 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 325
+
8.3 XENON FLUORIDES AS F DONORS AND OXIDANTS 305
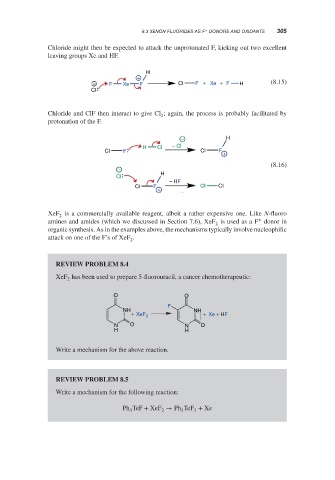
Chloride might then be expected to attack the unprotonated F, kicking out two excellent
leaving groups Xe and HF.
H
+
− F Xe F CI F + Xe + F H (8.15)
CI
Chloride and ClF then interact to give Cl ; again, the process is probably facilitated by
2
protonation of the F.
− H
H Cl − Cl
CI F CI F +
(8.16)
−
H
CI
− HF
CI F CI CI
+
XeF is a commercially available reagent, albeit a rather expensive one. Like N-fluoro
2
+
amines and amides (which we discussed in Section 7.6), XeF is used as a F donor in
2
organic synthesis. As in the examples above, the mechanisms typically involve nucleophilic
attack on one of the F’s of XeF .
2
REVIEW PROBLEM 8.4
XeF has been used to prepare 5-fluorouracil, a cancer chemotherapeutic:
2
O O
F
NH NH
+ XeF 2 + Xe + HF
N O N O
H H
Write a mechanism for the above reaction.
REVIEW PROBLEM 8.5
Write a mechanism for the following reaction:
Ph TeF + XeF → Ph TeF + Xe
3 2 3 3