Page 437 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 437
CHAP TER 1 4. 2 Decisional architecture
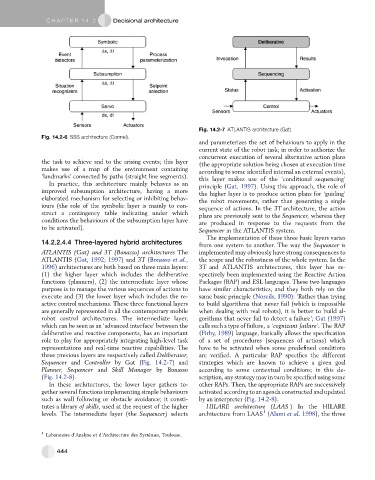
Fig. 14.2-7 ATLANTIS architecture (Gat).
Fig. 14.2-6 SSS architecture (Connel).
and parameterizes the set of behaviours to apply in the
current state of the robot task; in order to authorize the
concurrent execution of several alternative action plans
the task to achieve and to the arising events; this layer (the appropriate solution being chosen at execution time
makes use of a map of the environment containing according to some identified internal an external events),
‘landmarks’ connected by paths (straight line segments). this layer makes use of the ‘conditional sequencing’
In practice, this architecture mainly behaves as an principle (Gat, 1997). Using this approach, the role of
improved subsumption architecture, having a more the higher layer is to produce action plans for ‘guiding’
elaborated mechanism for selecting or inhibiting behav- the robot movements, rather than generating a single
iours (the role of the symbolic layer is mainly to con- sequence of actions. In the 3T architecture, the action
struct a contingency table indicating under which plans are previously sent to the Sequencer, whereas they
conditions the behaviours of the subsumption layer have are produced in response to the requests from the
to be activated).
Sequencer in the ATLANTIS system.
The implementation of these three basic layers varies
14.2.2.4.4 Three-layered hybrid architectures
from one system to another. The way the Sequencer is
ATLANTIS (Gat) and 3T (Bonasso) architectures The implemented may obviously have strong consequences to
ATLANTIS (Gat, 1992; 1997) and 3T (Bonasso et al., the scope and the robustness of the whole system. In the
1996) architectures are both based on three main layers: 3T and ATLANTIS architectures, this layer has re-
(1) the higher layer which includes the deliberative spectively been implemented using the Reactive Action
functions (planners), (2) the intermediate layer whose Packages (RAP) and ESL languages. These two languages
purpose is to manage the various sequences of actions to have similar characteristics, and they both rely on the
execute and (3) the lower layer which includes the re- same basic principle (Noreils, 1990): ‘Rather than trying
active control mechanisms. These three functional layers to build algorithms that never fail (which is impossible
are generally represented in all the contemporary mobile when dealing with real robots), it is better to build al-
robot control architectures. The intermediate layer, gorithms that never fail to detect a failure’; Gat (1997)
which can be seen as an ‘advanced interface’ between the calls such a type of failure, a ‘cognizant failure’. The RAP
deliberative and reactive components, has an important (Firby, 1989) language, basically allows the specification
role to play for appropriately integrating high-level task of a set of procedures (sequences of actions) which
representations and real-time reactive capabilities. The have to be activated when some predefined conditions
three previous layers are respectively called Deliberator, are verified. A particular RAP specifies the different
Sequencer and Controller by Gat (Fig. 14.2-7) and strategies which are known to achieve a given goal
Planner, Sequencer and Skill Manager by Bonasso according to some contextual conditions; in this de-
(Fig. 14.2-8). scription, any strategy may in turn be specified using some
In these architectures, the lower layer gathers to- other RAPs. Then, the appropriate RAPs are successively
gether several functions implementing simple behaviours activated according to an agenda constructed and updated
such as wall following or obstacle avoidance; it consti- by an interpreter (Fig. 14.2-8).
tutes a library of skills, used at the request of the higher HILARE architecture (LAAS ) In the HILARE
1
levels. The intermediate layer (the Sequencer) selects architecture from LAAS (Alami et al. 1998), the three
1
Laboratoire d’Analyse et d’Architecture des Syste `mes, Toulouse.
444