Page 440 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 440
Decisional architecture C HAPTER 14.2
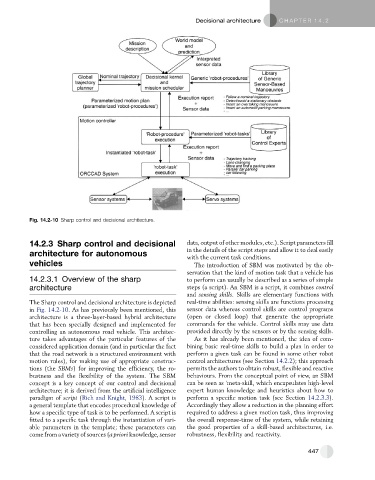
Fig. 14.2-10 Sharp control and decisional architecture.
14.2.3 Sharp control and decisional data, output of other modules, etc.). Script parameters fill
in the details of the script steps and allow it to deal easily
architecture for autonomous
with the current task conditions.
vehicles The introduction of SBM was motivated by the ob-
servation that the kind of motion task that a vehicle has
14.2.3.1 Overview of the sharp to perform can usually be described as a series of simple
architecture steps (a script). An SBM is a script, it combines control
and sensing skills. Skills are elementary functions with
The Sharp control and decisional architecture is depicted real-time abilities: sensing skills are functions processing
in Fig. 14.2-10. As has previously been mentioned, this sensor data whereas control skills are control programs
architecture is a three-layer-based hybrid architecture (open or closed loop) that generate the appropriate
that has been specially designed and implemented for commands for the vehicle. Control skills may use data
controlling an autonomous road vehicle. This architec- provided directly by the sensors or by the sensing skills.
ture takes advantages of the particular features of the As it has already been mentioned, the idea of com-
considered application domain (and in particular the fact bining basic real-time skills to build a plan in order to
that the road network is a structured environment with perform a given task can be found in some other robot
motion rules), for making use of appropriate construc- control architectures (see Section 14.2.2); this approach
tions (the SBMs) for improving the efficiency, the ro- permits the authors to obtain robust, flexible and reactive
bustness and the flexibility of the system. The SBM behaviours. From the conceptual point of view, an SBM
concept is a key concept of our control and decisional can be seen as ‘meta-skill, which encapsulates high-level
architecture; it is derived from the artificial intelligence expert human knowledge and heuristics about how to
paradigm of script (Rich and Knight, 1983). A script is perform a specific motion task (see Section 14.2.3.3).
a general template that encodes procedural knowledge of Accordingly they allow a reduction in the planning effort
how a specific type of task is to be performed. A script is required to address a given motion task, thus improving
fitted to a specific task through the instantiation of vari- the overall response-time of the system, while retaining
able parameters in the template; these parameters can the good properties of a skill-based architectures, i.e.
come from a variety of sources (a priori knowledge, sensor robustness, flexibility and reactivity.
447