Page 528 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 528
Terminology and overview of vehicle structure types C HAPTER 16.1
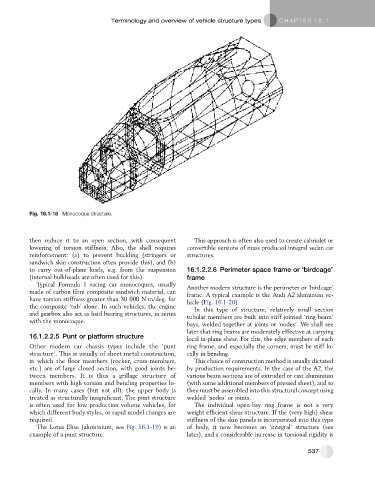
Fig. 16.1-18 Monocoque structure.
then reduce it to an open section, with consequent This approach is often also used to create cabriolet or
lowering of torsion stiffness. Also, the shell requires convertible versions of mass produced integral sedan car
reinforcement: (a) to prevent buckling (stringers or structures.
sandwich skin construction often provide this), and (b)
to carry out-of-plane loads, e.g. from the suspension 16.1.2.2.6 Perimeter space frame or ‘birdcage’
(internal bulkheads are often used for this). frame
Typical Formula 1 racing car monocoques, usually Another modern structure is the perimeter or ‘birdcage’
made of carbon fibre composite sandwich material, can frame. A typical example is the Audi A2 aluminum ve-
have torsion stiffness greater than 30 000 N m/deg. for hicle (Fig. 16.1-20).
the composite ‘tub’ alone. In such vehicles, the engine In this type of structure, relatively small section
and gearbox also act as load bearing structures, in series tubular members are built into stiff jointed ‘ring-beam’
with the monocoque.
bays, welded together at joints or ‘nodes’. We shall see
later that ring beams are moderately effective at carrying
16.1.2.2.5 Punt or platform structure local in-plane shear. For this, the edge members of each
Other modern car chassis types include the ‘punt ring frame, and especially the corners, must be stiff lo-
structure’. This is usually of sheet metal construction, cally in bending.
in which the floor members (rocker, cross-members, This choice of construction method is usually dictated
etc.) are of large closed section, with good joints be- by production requirements. In the case of the A2, the
tween members. It is thus a grillage structure of various beam sections are of extruded or cast aluminium
members with high torsion and bending properties lo- (with some additional members of pressed sheet), and so
cally. In many cases (but not all), the upper body is they must be assembled into this structural concept using
treated as structurally insignificant. The punt structure welded ‘nodes’ or joints.
is often used for low production volume vehicles, for The individual open-bay ring frame is not a very
which different body styles, or rapid model changes are weight efficient shear structure. If the (very high) shear
required. stiffness of the skin panels is incorporated into this type
The Lotus Elise (aluminium, see Fig. 16.1-19)isan of body, it now becomes an ‘integral’ structure (see
example of a punt structure. later), and a considerable increase in torsional rigidity is
537