Page 302 - Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 302
Adaptive Control of Mobile Robots 289
5
u 1 (rad/sec) 0
– 5
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Time (sec)
15
10
u 2 (m/sec) 5 0
– 5
– 10
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Time (sec)
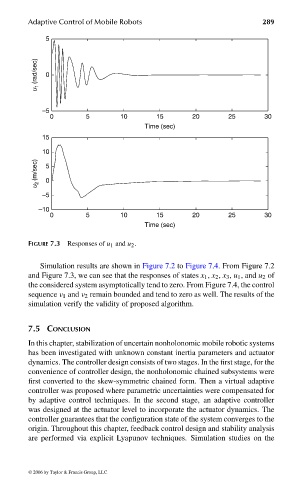
FIGURE 7.3 Responses of u 1 and u 2 .
Simulation results are shown in Figure 7.2 to Figure 7.4. From Figure 7.2
and Figure 7.3, we can see that the responses of states x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , u 1 , and u 2 of
the considered system asymptotically tend to zero. From Figure 7.4, the control
sequence ν 1 and ν 2 remain bounded and tend to zero as well. The results of the
simulation verify the validity of proposed algorithm.
7.5 CONCLUSION
In this chapter, stabilization of uncertain nonholonomic mobile robotic systems
has been investigated with unknown constant inertia parameters and actuator
dynamics. The controller design consists of two stages. In the first stage, for the
convenience of controller design, the nonholonomic chained subsystems were
first converted to the skew-symmetric chained form. Then a virtual adaptive
controller was proposed where parametric uncertainties were compensated for
by adaptive control techniques. In the second stage, an adaptive controller
was designed at the actuator level to incorporate the actuator dynamics. The
controller guarantees that the configuration state of the system converges to the
origin. Throughout this chapter, feedback control design and stability analysis
are performed via explicit Lyapunov techniques. Simulation studies on the
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
FRANKL: “dk6033_c007” — 2006/3/31 — 16:43 — page 289 — #23