Page 359 - Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 359
Map Building and SLAM Algorithms 349
(a) 1
0.5
0
A
– 0.5 B
– 1
– 1.5
– 0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
(b) 1
0.5
0
A
– 0.5 B
– 1
– 1.5
– 0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
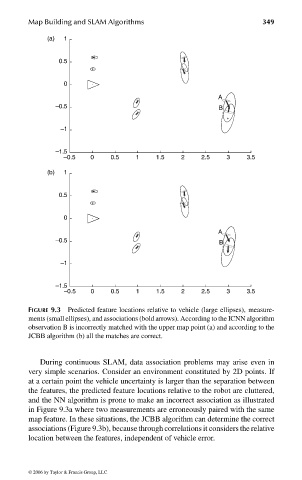
FIGURE 9.3 Predicted feature locations relative to vehicle (large ellipses), measure-
ments (small ellipses), and associations (bold arrows). According to the ICNN algorithm
observation B is incorrectly matched with the upper map point (a) and according to the
JCBB algorithm (b) all the matches are correct.
During continuous SLAM, data association problems may arise even in
very simple scenarios. Consider an environment constituted by 2D points. If
at a certain point the vehicle uncertainty is larger than the separation between
the features, the predicted feature locations relative to the robot are cluttered,
and the NN algorithm is prone to make an incorrect association as illustrated
in Figure 9.3a where two measurements are erroneously paired with the same
map feature. In these situations, the JCBB algorithm can determine the correct
associations (Figure 9.3b), because through correlations it considers the relative
location between the features, independent of vehicle error.
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
FRANKL: “dk6033_c009” — 2006/3/31 — 16:43 — page 349 — #19