Page 334 - Battery Reference Book
P. 334
Service time-voltage data 3015
1.5r
30
p 1.1
20
9 0.9 50 mA
10
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
0 Service time lh)
04 15 30 1 5 10 15 20
-Seconds -Minutes 4 (a) MN91M). 700 mA h, 1.5 V
(a) For immediate use 1.5r
0 3 6 9 12 15
Service time (h)
(b) MN1500, 1800 mA h, 1.5 V
1.5,
-Seconds -Minutes 4
(b) For wet stand
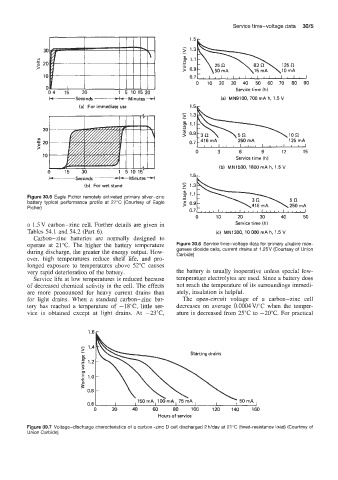
Figure 30.5 Eagle Picher remotely activated primary silver-zinc
battery typical performance profile at 27°C (Courtesy of Eagle ; 0.Y
250
Picher) \416 mA \ mA
0.7 a c 8 t 2 3 I 8 * a I a 0 t 8 I 5 a 9 1 J
0 10 20 30 40 50
a 1.5V carbon-zinc cell. Further details are given in Service time (hi
Tables 54.1 and 54.2 (Part 6). (c) MN1300, 10 Ow mA h, 1.5 V
Carbon-zinc batteries are normally designed to
operate at 21°C. The higher the battery temperature Figure 30.6 Service time-voltage data for primary alkaline man-
during discharge, the greater the energy output. How- ganese dioxide cells, current drains at 1.25V (Courtesy of Union
Carbide)
ever, high temperatures reduce shelf life, and pro-
longed exposure to temperatures above 52°C causes
very rapid deterioration of the battery. the battery is usually inoperative unless special low-
Service life at low temperatures is reduced because temperature electrolytes are used. Since a battery does
of decreased chemical activity in the cell. The effects not reach the temperature of its surroundings immedi-
are more pronounced for heavy current drains than ately, insulation is helpful.
for light drains. When a standard carbon-zinc bat- The open-circuit voltage of a carbon-zinc cell
tery has reached a temperature of -18"C, little ser- decreases on average O.O004V/"C when the temper-
vice is obtained except at light drains. At -23"C, ature is decreased from 25°C to -20°C. For practical
-
5: 1.4
m
0) Starting drains
- 2 1.2
9
m
5 1.0
P
0.8
0.6
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Hours of service
Figure 30.7 Voltage-discharge characteristics of a carbon-zinc 0 cell discharged 2 h/day at 21 "C (fixed-resistance load) (Courtesy of
Union Carbide)