Page 474 - Battery Reference Book
P. 474
The Eveready fast-charge cell (nickel-cadmium batteries) 4717
,.
g a '
12
(a) Concept 1
0 15 30 45 60 75 90 105
Time on charge (min)
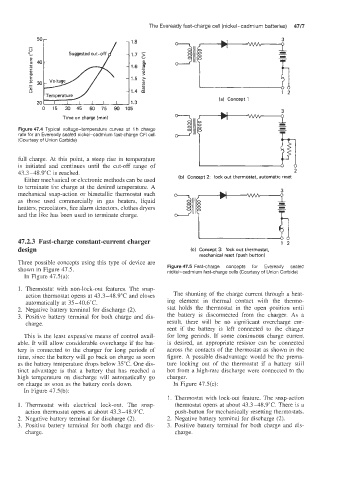
Figure 47.4 Typical voltage-temperature curves at 1 h charge
rate for an Eveready sealed nickel-cadmium fast-charge CFI cell
(Courtesy of Union Carbide)
full charge. At this point, a steep rise in temperature
is initiated and continues until the cut-off range of
43.3-48.9"C is reached. 2
Either mechanical or electronic methods can be used (b) Concept 2: lock out thermostat, automatic reset
to terminate tne charge at the desired temperature. A
mechanical snap-action or bimetallic thermostat such
as those used commercially in gas heaters, liquid
heaters, percollators, fire alarm detectors, clothes dryers
and the like has been used to terminate charge.
47.2.3 Fast-charge constant-current charger 12
design (c) Concept 3: lock out thermostat,
mechanical reset (push button)
Three possible concepts using this type of device are
shown in Figure 47.5. Figure 47.5 Fast-charge concepts for Eveready sealed
nickel-cadmium fast-charge cells (Courtesy of Union Carbide)
In Figure 47.5(a):
1. ThLermostat with non-lock-out features. The snap-
action thermostat opens at 43.3-48.9"C and closes The shunting of the charge current through a heat-
automatically at 35 -40.6"C. ing element in thermal contact with the thermo-
2. Negative battery terminal for discharge (2). stat holds the thermostat in the open position until
3. Positive battery terminal for both charge and dis- the battery is disconnected from the charger. As a
charge. result, there will be no signiscant overcharge cur-
rent if the battery is left connected to the charger
This is the least expensive means of control avail- for long periods. If some continuous charge current
able. It will allow considerable overcharge if the bat- is desired, an appropriate resistor can be connected
tery is connected to the charger for long periods of across the contacts of the thermostat as shown in the
time, since the battery will go back on charge as soon figure. A possible disadvantage would be the prema-
as the battery temperature drops below 35°C. One dis- ture locking out of the thermostat if a battery still
tinct advantage is that a battery that has reached a hot from a high-rate discharge were connected to the
high temperature on discharge will automatically go charger.
on charge as soon as the battery cools down. In Figure 47.5(c):
In Figure 47.5(b):
1. Thermostat with lock-out feature. The snapaction
1. Thermostat with electrical lock-out. The snap- thermostat opens at about 43.3-48.9"C. There is a
action thermostat opens at about 43.3-48.9"C. push-button for mechanically resetting thermostats.
2. Negative battery terminal for discharge (2). 2. Negative battery terminal for discharge (2).
3. Positive battery terminal for both charge and dis- 3. Positive battery terminal for both charge and dis-
charge. charge.