Page 475 - Battery Reference Book
P. 475
47/8 Constant-current charging
The snap-action thermostat would cut off all charge 47.3 Types of constant-current
currents. This concept might be useful in an application charging
where high-rate charge was not normally needed, but
would be useful at certain times. A charger could There are many constant-current methods that per-
be designed to provide more moderate charging such mit satisfactory charging of sealed nickel-cadmium
as the C/10 rate, unless the user pushed the reset batteries. These methods differ in the length of time
button when a fast charge was required (as shown required to charge, the complexity of the circuits used
in the figure). Again a heated battery from high-rate and the various techniques for charging with maximum
discharge would necessitate a wait until the thermostat safety and reliability. The following charging systems
could be reset. are worthy of mention (see Table 47.1):
A second means of terminating the charge on
the battery at the desired cut-off temperature is 1. Normal rate charge.
through the use of temperature-responsive electronic 2. Accelerated charge.
circuitry. In essence, this circuit will electronically 3. Controlled rapid charge: timed, voltage-time con-
terminate charge when the desired temperature is trol, voltage-tempei-ature control.
reached through the use of a sensing element and 4. Ultra-rapid charge.
switching-type devices. A possible electronic circuit 5. Uncontrolled rapid charge.
for this type of charge control is shown in Figure 47.6. 6. Low-temperature charge.
The time to reach cut-off and the period of cycling 'on' 7. Permanent or floating charge.
and 'off' depend on charge rate, battery packaging and
ambient temperature. The various methods of charging of sealed
nickel-cadmium cells and batteries are discussed
briefly below.
47.3.1 Normal constant-current charging
This is the method recommended by all battery manu-
facturers for the charging of sealed nickel-cadmium
batteries at the normal (i.e. unaccelerated) rate of
charge.
1-44 current, where the initial current (when the battery is
It is permissible to use a nominal constant
discharged) is not critical, provided the Zlo rate is not
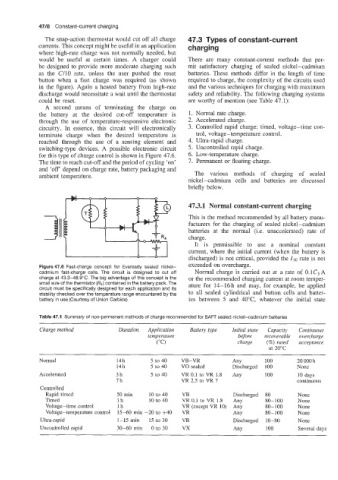
Figure 47.6 Fast-charge concept for Eveready sealed nickel- exceeded on overcharge.
cadmium fast-charge cells. The circuit is designed to cut off Normal charge is carried out at a rate of 0.1Cs A
charge at 43.3-48.9"C. The big advantage of this concept is the or the recommended charging current at room ternper-
small size of the thermistor (R4) contained in the battery pack. The ature for 14-16h and may, for example, be applied
circuit must be specifically designed for each application and its
stability checked over the temperature range encountered by the to all sealed cylindrical and button cells and batter-
battery in use (Courtesy of Union Carbide) ies between 5 and 40"C, whatever the initial state
Table 47.1 Summary of non-permanent methods of charge recommended for SAFT sealed nickel-cadmium batteries
Charge method Duration Application Battely type Initial state Capacit): Continuous
temperature before recoverable overcharge
("C) charge (%) rated acceptance
at 20°C
Normal 14h 5 to 40 VB -VR Any 100 20 000 h
14h 5 to 40 VO sealed Discharged 100 None
Accelerated 3h 5 to 40 VR 0.1 to VR 1.8 Any 100 10 days
7h VR 2.5 to VR 7 continuous
Controlled
Rapid timed 50 min 10 to 40 VB Discharged 80 None
Timed lh 10 to 40 VR 0.1 to VR 1.8 Any 80-100 None
Voltage-time control lh VR (except VR 10) Any 80-100 None
Voltage- temperature control 15-60 min -20 to +40 VR Any 80-100 None
Ultra-rapid 1-15 min 15 to 30 VR Discharged 10-80 None
Uncontrolled rapid 30-60 min 0 to 30 vx Any 100 Several days