Page 134 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 134
Using Primitive Logic Functions to Build More Complex Functions w 1 15
result is that the 1 from causes the 0 at 180 which is fed back to
1917, and the O on the set input combined with the O from causes
the I at [m which is fed back to 17.
Thus, the latch5 has now been placed in its reset condition, and a self-
sustaining loop has been established. Even though both the reset and set
inputs are now inactive, the q output remains at 0, indicating that reset was
the last input to be in its active state. Once the function has been placed in its
reset condition, any subsequent activity on the reset input will have no effect on
the outputs, which means that the only way to affect the function is by means
of its set input.
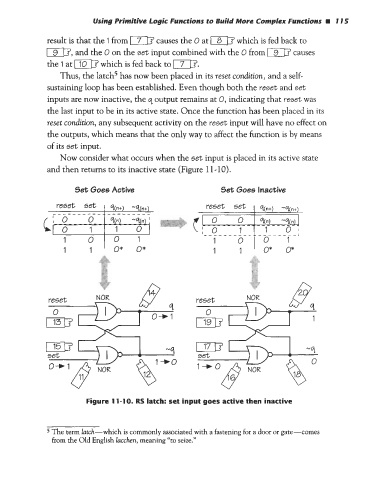
Now consider what occurs when the set input is placed in its active state
and then returns to its inactive state (Figure 11-10>.
6et Goes Active 4et Goes Inactive
1 1 ’ O* o*
set
1 +o
/6 NOK
Figure 11-10. RS latch: set input goes active then inactive
5 The term latch-which is commonly associated with a fastening for a door or gate-comes
from the Old English lacchen, meaning “to seize.”