Page 383 - Biaxial Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture
P. 383
The Enuironment Effect on Fatigue Crack Growth Rates in 7049 Aluminium Alloy at _.. 367
The fatigue experiments were performed on a servo-hydraulic testing machine under
constant load control with 30 Hz sine wave loading, in ambient air at 20 "C, 50% HR or in
vacuum (2.6~10" Pa). The fatigue crack growth curves were obtained by shedding the load in
steps of 7% until a crack growth rate approximately 1.3xlO-" dcycle was obtained. In the
threshold regime the load was reduced 3.5 % only and Aa was less than 0.04 mm during
3x106 cycles at the crack growth rate of 1.3x10-" dcycle. After reaching the threshold, the
load was increased again to obtain higher crack growth rates. This procedure allowed to get
the entire crack growth curve from one specimen. Crack propagation was detected by
observing the polished specimen surfaces with a microscope at a magnification of 50x.
Calculations of the SIF and dddN were performed according to the ASTM E-674 standard.
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
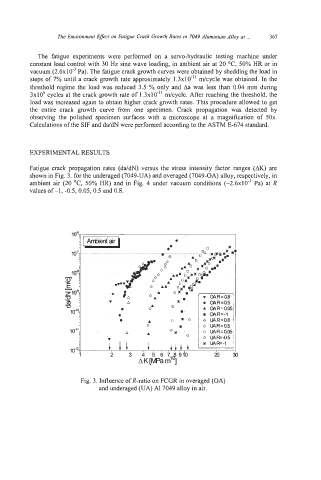
Fatigue crack propagation rates (dddN) versus the stress intensity factor ranges (AK) are
shown in Fig. 3. for the underaged (7049-UA) and overaged (7049-OA) alloy, respectively, in
ambient air (20 "C, 50% HR) and in Fig. 4 under vacuum conditions (-2.6~10'~ Pa) at R
valuesof-1, -0.5,0.05, 0.5 andO.8.
Fig. 3. Influence of R-ratio on FCGR in overaged (OA)
and underaged (UA) A1 7049 alloy in air.