Page 264 - Big Data Analytics for Intelligent Healthcare Management
P. 264
10.7 MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS AND SCORING FUNCTIONS 257
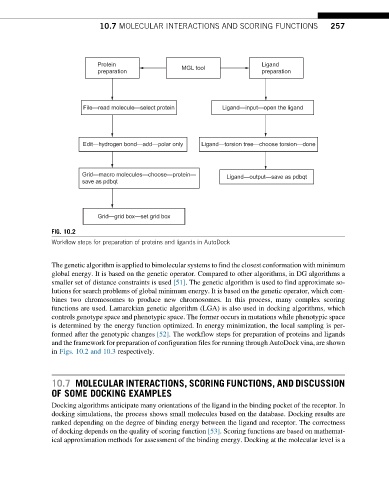
Protein MGL tool Ligand
preparation preparation
File—read molecule—select protein Ligand—input—open the ligand
Edit—hydrogen bond—add—polar only Ligand—torsion tree—choose torsion—done
Grid—macro molecules—choose—protein— Ligand—output—save as pdbqt
save as pdbqt
Grid—grid box—set grid box
FIG. 10.2
Workflow steps for preparation of proteins and ligands in AutoDock
The genetic algorithm is applied to bimolecular systems to find the closest conformation with minimum
global energy. It is based on the genetic operator. Compared to other algorithms, in DG algorithms a
smaller set of distance constraints is used [51]. The genetic algorithm is used to find approximate so-
lutions for search problems of global minimum energy. It is based on the genetic operator, which com-
bines two chromosomes to produce new chromosomes. In this process, many complex scoring
functions are used. Lamarckian genetic algorithm (LGA) is also used in docking algorithms, which
controls genotype space and phenotypic space. The former occurs in mutations while phenotypic space
is determined by the energy function optimized. In energy minimization, the local sampling is per-
formed after the genotypic changes [52]. The workflow steps for preparation of proteins and ligands
and the framework for preparation of configuration files for running through AutoDock vina, are shown
in Figs. 10.2 and 10.3 respectively.
10.7 MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS, SCORING FUNCTIONS, AND DISCUSSION
OF SOME DOCKING EXAMPLES
Docking algorithms anticipate many orientations of the ligand in the binding pocket of the receptor. In
docking simulations, the process shows small molecules based on the database. Docking results are
ranked depending on the degree of binding energy between the ligand and receptor. The correctness
of docking depends on the quality of scoring function [53]. Scoring functions are based on mathemat-
ical approximation methods for assessment of the binding energy. Docking at the molecular level is a