Page 267 - Big Data Analytics for Intelligent Healthcare Management
P. 267
260 CHAPTER 10 COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY APPROACH ON GENETIC
DISORDER
Table 10.4 Binding Energy, Binding Residue, Bond Name, and Bond Length of Interactions
Between Targeted Proteins With Drugs for Alzheimer’s Disease in a Molecular Docking
Analysis.—cont’d
Binding Bond
Energy Binding Length
˚
Protein Name Drug Name (kcal/mol) Residues Name of the Bond (A)
Cyclin-dependent-like Alsterpaullone 9.6 ASP86 Electrostatic bond 3.92707
kinase 5 LEU133 Hydrophobic bond 3.77419
PHE80 Hydrophobic bond 5.1393
VAL18 Hydrophobic bond 4.94964
LEU133 Hydrophobic bond 5.45131
VAL18 Hydrophobic bond 4.92333
ALA31 Hydrophobic bond 4.77214
VAL64 Hydrophobic bond 5.38558
SU9516 7.4 ASN144 Hydrogen bond 3.10501
ILE10 Hydrogen bond 3.72764
LEU133 Hydrophobic bond 3.56806
LEU133 Hydrophobic bond 5.35007
VAL18 Hydrophobic bond 4.92563
VAL64 Hydrophobic bond 5.24212
Interactions
van der Waals Pi-Sigma
Conventional hydrogen bond Pi-Alkyl
Pi-Anion
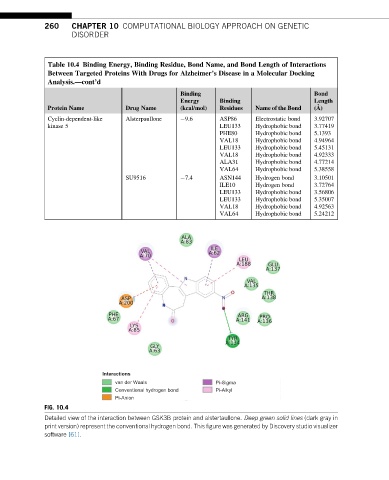
FIG. 10.4
Detailed view of the interaction between GSK3B protein and alstertaullone. Deep green solid lines (dark gray in
print version) represent the conventional hydrogen bond. This figure was generated by Discovery studio visualizer
software [61].