Page 265 - Big Data Analytics for Intelligent Healthcare Management
P. 265
258 CHAPTER 10 COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY APPROACH ON GENETIC
DISORDER
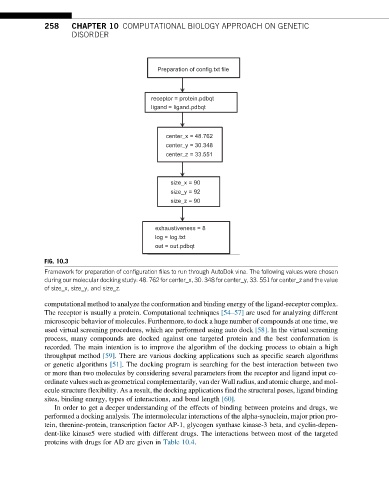
Preparation of config.txt file
receptor = protein.pdbqt
ligand = ligand.pdbqt
center_x = 48.762
center_y = 30.348
center_z = 33.551
size_x = 90
size_y = 92
size_z = 90
exhaustiveness = 8
log = log.txt
out = out.pdbqt
FIG. 10.3
Framework for preparation of configuration files to run through AutoDok vina. The following values were chosen
during our molecular docking study: 48. 762 for center_x, 30. 348 for center_y, 33. 551 for center_z and the value
of size_x, size_y, and size_z.
computational method to analyze the conformation and binding energy of the ligand-receptor complex.
The receptor is usually a protein. Computational techniques [54–57] are used for analyzing different
microscopic behavior of molecules. Furthermore, to dock a huge number of compounds at one time, we
used virtual screening procedures, which are performed using auto dock [58]. In the virtual screening
process, many compounds are docked against one targeted protein and the best conformation is
recorded. The main intention is to improve the algorithm of the docking process to obtain a high
throughput method [59]. There are various docking applications such as specific search algorithms
or genetic algorithms [51]. The docking program is searching for the best interaction between two
or more than two molecules by considering several parameters from the receptor and ligand input co-
ordinate values such as geometrical complementarily, van der Wall radius, and atomic charge, and mol-
ecule structure flexibility. As a result, the docking applications find the structural poses, ligand binding
sites, binding energy, types of interactions, and bond length [60].
In order to get a deeper understanding of the effects of binding between proteins and drugs, we
performed a docking analysis. The intermolecular interactions of the alpha-synuclein, major prion pro-
tein, threnine-protein, transcription factor AP-1, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, and cyclin-depen-
dent-like kinase5 were studied with different drugs. The interactions between most of the targeted
proteins with drugs for AD are given in Table 10.4.