Page 70 - Big Data Analytics for Intelligent Healthcare Management
P. 70
4.3 DATASET AND METHODOLOGIES 63
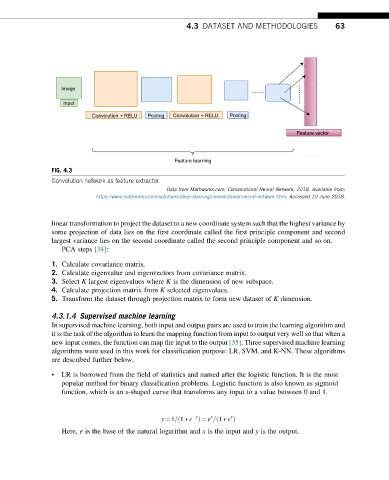
Image
Input
Convolution + RELU Pooling Convolution + RELU Pooling
Feature vector
Feature learning
FIG. 4.3
Convolution network as feature extractor.
Data from Mathworks.com, Convolutional Neural Network, 2018. Available from:
https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning/convolutional-neural-network.html. Accessed 10 June 2018.
linear transformation to project the dataset to a new coordinate system such that the highest variance by
some projection of data lies on the first coordinate called the first principle component and second
largest variance lies on the second coordinate called the second principle component and so on.
PCA steps [34]:
1. Calculate covariance matrix.
2. Calculate eigenvalue and eigenvectors from covariance matrix.
3. Select K largest eigenvalues where K is the dimension of new subspace.
4. Calculate projection matrix from K selected eigenvalues.
5. Transform the dataset through projection matrix to form new dataset of K dimension.
4.3.1.4 Supervised machine learning
In supervised machine learning, both input and output pairs are used to train the learning algorithm and
it is the task of the algorithm to learn the mapping function from input to output very well so that when a
new input comes, the function can map the input to the output [35]. Three supervised machine learning
algorithms were used in this work for classification purpose: LR, SVM, and K-NN. These algorithms
are described further below.
• LR is borrowed from the field of statistics and named after the logistic function. It is the most
popular method for binary classification problems. Logistic function is also known as sigmoid
function, which is an s-shaped curve that transforms any input to a value between 0 and 1.
x x x
ð
y ¼ 1= 1+ e Þ ¼ e = 1+ e Þ
ð
Here, e is the base of the natural logarithm and x is the input and y is the output.