Page 134 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 134
110 5 Multi-Enzyme Systems and Cascade Reactions Involving Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenases
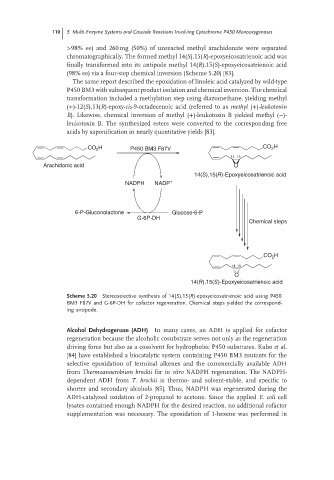
>98% ee) and 260 mg (50%) of unreacted methyl arachidonate were separated
chromatographically. The formed methyl 14(S),15(R)-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid was
finally transformed into its antipode methyl 14(R),15(S)-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
(98% ee) via a four-step chemical inversion (Scheme 5.20) [83].
The same report described the epoxidation of linoleic acid catalyzed by wild-type
P450 BM3 with subsequent product isolation and chemical inversion. The chemical
transformation included a methylation step using diazomethane, yielding methyl
(+)-12(S),13(R)-epoxy-cis-9-octadecenoic acid (referred to as methyl (+)-leukotoxin
B). Likewise, chemical inversion of methyl (+)-leukotoxin B yielded methyl (−)-
leukotoxin B. The synthesized esters were converted to the corresponding free
acids by saponification in nearly quantitative yields [83].
CO H P450 BM3 F87V CO 2 H
2
14 15
Arachidonic acid O
14(S),15(R)-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
NADPH NADP +
6-P-Gluconolactone Glucose-6-P
G-6P-DH
Chemical steps
CO 2 H
14 15
O
14(R),15(S)-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
Scheme 5.20 Stereoselective synthesis of 14(S),15(R)-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid using P450
BM3 F87V and G-6P-DH for cofactor regeneration. Chemical steps yielded the correspond-
ing antipode.
Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH) In many cases, an ADH is applied for cofactor
regeneration because the alcoholic cosubstrate serves not only as the regeneration
driving force but also as a cosolvent for hydrophobic P450 substrates. Kubo et al.
[84] have established a biocatalytic system containing P450 BM3 mutants for the
selective epoxidation of terminal alkenes and the commercially available ADH
from Thermoanaerobium brockii for in vitro NADPH regeneration. The NADPH-
dependent ADH from T. brockii is thermo- and solvent-stable, and specific to
shorter and secondary alcohols [85]. Thus, NADPH was regenerated during the
ADH-catalyzed oxidation of 2-propanol to acetone. Since the applied E. coli cell
lysates contained enough NADPH for the desired reaction, no additional cofactor
supplementation was necessary. The epoxidation of 1-hexene was performed in