Page 146 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 146
122 5 Multi-Enzyme Systems and Cascade Reactions Involving Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenases
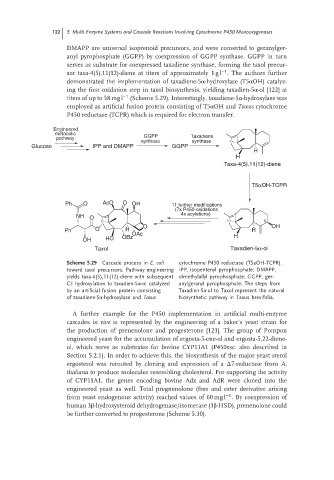
DMAPP are universal isoprenoid precursors, and were converted to geranylger-
anyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) by coexpression of GGPP synthase. GGPP in turn
serves as substrate for coexpressed taxadiene synthase, forming the taxol precur-
−1
sor taxa-4(5),11(12)-diene at titers of approximately 1 g l . The authors further
demonstrated the implementation of taxadiene-5α-hydroxylase (T5αOH) catalyz-
ing the first oxidation step in taxol biosynthesis, yielding taxadien-5α-ol [122] at
titers of up to 58 mg l −1 (Scheme 5.29). Interestingly, taxadiene-5α-hydroxylase was
employed as artificial fusion protein consisting of T5αOH and Taxus cytochrome
P450 reductase (TCPR) which is required for electron transfer.
Engineered
metabolic GGPP Taxadiene
pathway
synthase synthase
Glucose IPP and DMAPP GGPP
H
H
Taxa-4(5),11(12)-diene
T5αOH-TCPR
Ph O AcO O OH 11 further modifications
(7x P450-oxidations
4x acylations)
NH O
5
O OH
Ph O H OAc H
OH HO OBz H
Taxol Taxadien-5α-ol
Scheme 5.29 Cascade process in E. coli cytochrome P450 reductase (T5aOH-TCPR).
toward taxol precursors. Pathway engineering IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; DMAPP,
yields taxa-4(5),11(12)-diene with subsequent dimethylallyl pyrophosphate; GGPP, ger-
C5 hydroxylation to taxadien-5α-ol catalyzed anylgeranyl pyrophosphate. The steps from
by an artificial fusion protein consisting Taxadien-5a-ol to Taxol represent the natural
of taxadiene-5α-hydroxylase and Taxus biosynthetic pathway in Taxus brevifolia.
A further example for the P450 implementation in artificial multi-enzyme
cascades in vivo is represented by the engineering of a baker’s yeast strain for
the production of prenenolone and progesterone [123]. The group of Pompon
engineered yeast for the accumulation of ergosta-5-ene-ol and ergosta-5,22-diene-
ol, which serve as substrates for bovine CYP11A1 (P450ssc: also described in
Section 5.2.1). In order to achieve this, the biosynthesis of the major yeast sterol
ergosterol was rerouted by cloning and expression of a Δ7-reductase from A.
thaliana to produce molecules resembling cholesterol. For supporting the activity
of CYP11A1, the genes encoding bovine Adx and AdR were cloned into the
engineered yeast as well. Total pregnenolone (free and ester derivative arising
−1
from yeast endogenous activity) reached values of 60 mg l . By coexpression of
human 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/isomerase (3β-HSD), prenenolone could
be further converted to progesterone (Scheme 5.30).