Page 187 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 187
7.2 Dihydropyrimidinase 163
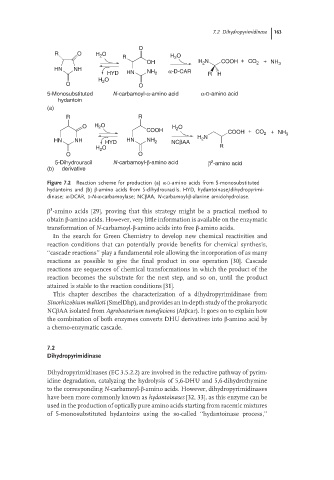
O
R O H O R H O
2
2
OH H 2 N COOH + CO 2 + NH 3
HN NH α-D-CAR
HYD HN NH 2 R H
H O
2
O O
5-Monosubstituted N-carbamoyl-α-amino acid α-D-amino acid
hydantoin
(a)
R R
O H O H 2 O
2
COOH COOH + CO 2 + NH
N 3
H 2
HN NH HYD HN NH 2 NCβAA
O R
H 2
O O
2
5-Dihydrouracil N-carbamoyl-β-amino acid β -amino acid
(b) derivative
Figure 7.2 Reaction scheme for production (a) α-D-amino acids from 5-monosubstituted
hydantoins and (b) β-amino acids from 5-dihydrouracils. HYD, hydantoinase/dihydropyrimi-
dinase; α-DCAR, D-N-α-carbamoylase; NCβAA, N-carbamoyl-β-alanine amidohydrolase.
3
β -amino acids [29], proving that this strategy might be a practical method to
obtain β-amino acids. However, very little information is available on the enzymatic
transformation of N-carbamoyl-β-amino acids into free β-amino acids.
In the search for Green Chemistry to develop new chemical reactivities and
reaction conditions that can potentially provide benefits for chemical synthesis,
‘‘cascade reactions’’ play a fundamental role allowing the incorporation of as many
reactions as possible to give the final product in one operation [30]. Cascade
reactions are sequences of chemical transformations in which the product of the
reaction becomes the substrate for the next step, and so on, until the product
attained is stable to the reaction conditions [31].
This chapter describes the characterization of a dihydropyrimidinase from
Sinorhizobium meliloti (SmelDhp), and provides an in-depth study of the prokaryotic
NCβAA isolated from Agrobacterium tumefaciens (Atβcar). It goes on to explain how
the combination of both enzymes converts DHU derivatives into β-amino acid by
a chemo-enzymatic cascade.
7.2
Dihydropyrimidinase
Dihydropyrimidinases (EC 3.5.2.2) are involved in the reductive pathway of pyrim-
idine degradation, catalyzing the hydrolysis of 5,6-DHU and 5,6-dihydrothymine
to the corresponding N-carbamoyl-β-amino acids. However, dihydropyrimidinases
have been more commonly known as hydantoinases [32, 33], as this enzyme can be
used in the production of optically pure amino acids starting from racemic mixtures
of 5-monosubstituted hydantoins using the so-called ‘‘hydantoinase process,’’