Page 195 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 195
7.3 N-Carbamoyl-β-Alanine Amidohydrolase 171
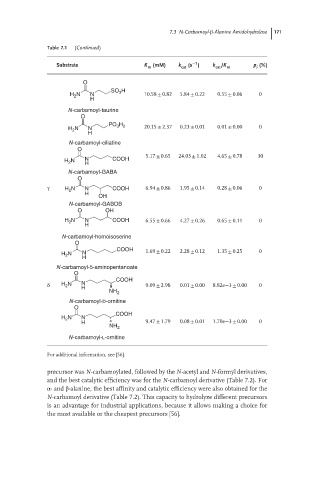
Table 7.1 (Continued)
−1
Substrate K m (mM) k cat (s ) k cat /K m p (%)
i
O
SO H
H N N 3 10.58 ± 0.82 5.84 ± 0.22 0.55 ± 0.06 0
2
H
N-carbamoyl-taurine
O
PO H
3 2
H N N 20.15 ± 2.37 0.23 ± 0.01 0.01 ± 0.00 0
2
H
N-carbamoyl-ciliatine
O
5.17 ± 0.65 24.03 ± 1.02 4.65 ± 0.78 30
H N N COOH
2
H
N-carbamoyl-GABA
O
γ H N N COOH 6.94 ± 0.86 1.95 ± 0.14 0.28 ± 0.06 0
2
H
OH
N-carbamoyl-GABOB
O OH
H 2 N N COOH 6.55 ± 0.66 4.27 ± 0.26 0.65 ± 0.11 0
H
N-carbamoyl-homoisoserine
O
COOH 1.69 ± 0.22 2.28 ± 0.12 1.35 ± 0.25 0
H N N
2
H
N-carbamoyl-5-aminopentanoate
O
COOH
δ H N N 9.09 ± 2.98 0.01 ± 0.00 8.82e−3 ± 0.00 0
2
H
NH 2
N-carbamoyl-D-ornitine
O
COOH
H N N
2
H 9.47 ± 1.79 0.08 ± 0.01 1.70e−3 ± 0.00 0
NH 2
N-carbamoyl-L-ornitine
For additional information, see [56].
precursor was N-carbamoylated, followed by the N-acetyl and N-formyl derivatives,
and the best catalytic efficiency was for the N-carbamoyl derivative (Table 7.2). For
α-and β-alanine, the best affinity and catalytic efficiency were also obtained for the
N-carbamoyl derivative (Table 7.2). This capacity to hydrolyze different precursors
is an advantage for industrial applications, because it allows making a choice for
the most available or the cheapest precursors [56].