Page 235 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 235
9.2 Enzyme-Catalyzed Stereoselective Reactions in Continuous-Flow Systems 211
EtOAc NH-COMe
Microextractor COOH
NH-COMe D-Ac-Phe (in EtOAc)
COOH
DL-Ac-Phe
Acylase
+
capillary reactor NH CI −
H O 3
2
HCl in H 2 O
COOH
L-Phe·HCI (in H O)
2
Acylase – polylysine co-CLEA
membrane layer
Tube
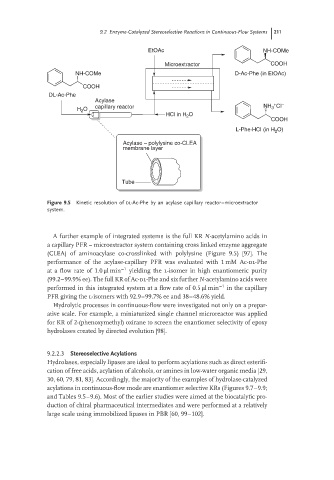
Figure 9.5 Kinetic resolution of DL-Ac-Phe by an acylase capillary reactor–microextractor
system.
A further example of integrated systems is the full KR N-acetylamino acids in
a capillary PFR – microextractor system containing cross linked enzyme aggregate
(CLEA) of aminoacylase co-crosslinked with polylysine (Figure 9.5) [97]. The
performance of the acylase-capillary PFR was evaluated with 1 mM Ac-dl-Phe
at a flow rate of 1.0 μlmin −1 yielding the l-isomer in high enantiomeric purity
(99.2–99.9% ee). The full KR of Ac-dl-Phe and six further N-acetylamino acids were
performed in this integrated system at a flow rate of 0.5 μlmin −1 in the capillary
PFR giving the l-isomers with 92.9–99.7% ee and 38–48.6% yield.
Hydrolytic processes in continuous-flow were investigated not only on a prepar-
ative scale. For example, a miniaturized single channel microreactor was applied
for KR of 2-(phenoxymethyl) oxirane to screen the enantiomer selectivity of epoxy
hydrolases created by directed evolution [98].
9.2.2.3 Stereoselective Acylations
Hydrolases, especially lipases are ideal to perform acylations such as direct esterifi-
cation of free acids, acylation of alcohols, or amines in low-water organic media [29,
30, 60, 79, 81, 83]. Accordingly, the majority of the examples of hydrolase-catalyzed
acylations in continuous-flow mode are enantiomer selective KRs (Figures 9.7–9.9;
and Tables 9.5–9.6). Most of the earlier studies were aimed at the biocatalytic pro-
duction of chiral pharmaceutical intermediates and were performed at a relatively
large scale using immobilized lipases in PBR [60, 99–102].