Page 237 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 237
9.2 Enzyme-Catalyzed Stereoselective Reactions in Continuous-Flow Systems 213
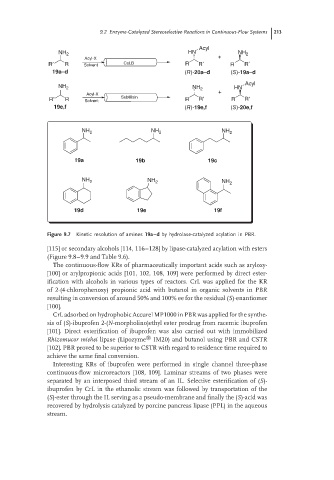
Acyl
NH 2 HN NH 2
Acyl-X +
R′ R Solvent CaLB R R′ R R′
19a–d (R)-20a–d (S)-19a–d
Acyl
NH 2 NH 2 HN
Acyl-X +
R′ R Solvent Subtilisin R R′ R R′
19e,f (R)-19e,f (S)-20e,f
NH 2 NH 2 NH 2
19a 19b 19c
NH 2 NH 2 NH 2
19d 19e 19f
Figure 9.7 Kinetic resolution of amines 19a–d by hydrolase-catalyzed acylation in PBR.
[115] or secondary alcohols [114, 116–128] by lipase-catalyzed acylation with esters
(Figure 9.8–9.9 and Table 9.6).
The continuous-flow KRs of pharmaceutically important acids such as aryloxy-
[100] or arylpropionic acids [101, 102, 108, 109] were performed by direct ester-
ification with alcohols in various types of reactors. CrL was applied for the KR
of 2-(4-chlorophenoxy) propionic acid with butanol in organic solvents in PBR
resulting in conversion of around 50% and 100% ee for the residual (S)-enantiomer
[100].
CrL adsorbed on hydrophobic Accurel MP1000 in PBR was applied for the synthe-
sis of (S)-ibuprofen 2-(N-morpholino)ethyl ester prodrug from racemic ibuprofen
[101]. Direct esterification of ibuprofen was also carried out with immobilized
Rhizomucor miehei lipase (Lipozyme ® IM20) and butanol using PBR and CSTR
[102]. PBR proved to be superior to CSTR with regard to residence time required to
achieve the same final conversion.
Interesting KRs of ibuprofen were performed in single channel three-phase
continuous-flow microreactors [108, 109]. Laminar streams of two phases were
separated by an interposed third stream of an IL. Selective esterification of (S)-
ibuprofen by CrL in the ethanolic stream was followed by transportation of the
(S)-ester through the IL serving as a pseudo-membrane and finally the (S)-acid was
recovered by hydrolysis catalyzed by porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) in the aqueous
stream.