Page 388 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 388
364 17 Enzymatic Generation of Sialoconjugate Diversity
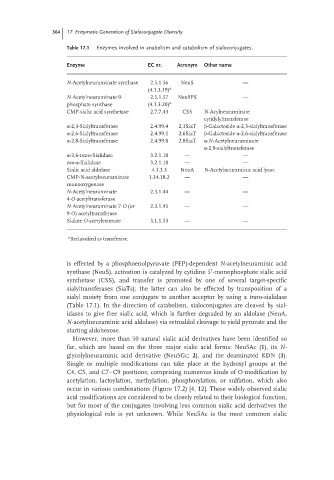
Table 17.1 Enzymes involved in anabolism and catabolism of sialoconjugates.
Enzyme EC nr. Acronym Other name
N-Acetylneuraminate synthase 2.5.1.56 NeuS —
(4.1.3.19) a
N-Acetylneuraminate-9- 2.5.1.57 Neu9PS —
phosphate synthase (4.1.3.20) a
CMP-sialic acid synthetase 2.7.7.43 CSS N-Acylneuraminate
cytidylyltransferase
α-2,3-Sialyltransferase 2.4.99.4 2,3SiaT β-Galactoside α-2,3-sialyltransferase
α-2,6-Sialyltransferase 2.4.99.1 2,6SiaT β-Galactoside α-2,6-sialyltransferase
α-2,8-Sialyltransferase 2.4.99.8 2,8SiaT α-N-Acetylneuraminate
α-2,8-sialyltransferase
α-2,6-trans-Sialidase 3.2.1.18 — —
exo-α-Sialidase 3.2.1.18 — —
Sialic acid aldolase 4.1.3.3 NeuA N-Acetylneuraminic acid lyase
CMP-N-acetylneuraminate 1.14.18.2 — —
monooxygenase
N-Acetylneuraminate 2.3.1.44 — —
4-O-acetyltransferase
N-Acetylneuraminate 7-O (or 2.3.1.45 — —
9-O)-acetyltransferase
Sialate O-acetylesterase 3.1.1.53 — —
a
Reclassified as transferase.
is effected by a phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-dependent N-acetylneuraminic acid
′
synthase (NeuS), activation is catalyzed by cytidine 5 -monophosphate sialic acid
synthetase (CSS), and transfer is promoted by one of several target-specific
sialyltransferases (SiaTs); the latter can also be effected by transposition of a
sialyl moiety from one conjugate to another acceptor by using a trans-sialidase
(Table 17.1). In the direction of catabolism, sialoconjugates are cleaved by sial-
idases to give free sialic acid, which is further degraded by an aldolase (NeuA,
N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase) via retroaldol cleavage to yield pyruvate and the
starting aldohexose.
However, more than 50 natural sialic acid derivatives have been identified so
far, which are based on the three major sialic acid forms: Neu5Ac (1), its N-
glycolylneuraminic acid derivative (Neu5Gc; 2), and the deaminated KDN (3).
Single or multiple modifications can take place at the hydroxyl groups at the
C4, C5, and C7–C9 positions, comprising numerous kinds of O-modification by
acetylation, lactoylation, methylation, phosphorylation, or sulfation, which also
occur in various combinations (Figure 17.2) [4, 12]. These widely observed sialic
acid modifications are considered to be closely related to their biological function,
but for most of the conjugates involving less common sialic acid derivatives the
physiological role is yet unknown. While Neu5Ac is the most common sialic