Page 392 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 392
368 17 Enzymatic Generation of Sialoconjugate Diversity
synthetic probes for the Leloir-path sialyltransfer enzymes and have been used in
the preparation of natural sialoconjugates and non-natural neo-sialoconjugates is
presented in Scheme 17.3.
17.2.1
Synthesis of Sialic Acid Diversity
The extended nine-carbon backbone of sialic acids can be constructed from hexose
building blocks by aldol addition of a pyruvate unit. Synthetic studies for sialic
acid and its modifications have extensively used the catabolic enzyme NeuA,
which catalyzes the reversible addition of pyruvate (5)to N-acetyl-d-mannosamine
(ManNAc, 4) to form the parent sialic acid Neu5Ac (1; Scheme 17.4) [16, 17,
19]. These freely reversible aldol additions have equilibrium constants in favor of
cleavage direction [20], which requires that synthetic reactions have to be driven
by an excess of one substrate to achieve satisfactory conversions; for economic
reasons, this usually is 5. In contrast, NeuS utilizes PEP (6) as a high-energy
nucleophile, which upon C–C bond formation releases inorganic phosphate and
thus renders the addition essentially irreversible [21]. Despite its considerable
synthetic potential, NeuS still is an orphan catalyst which so far has been less
studied for preparative applications [22].
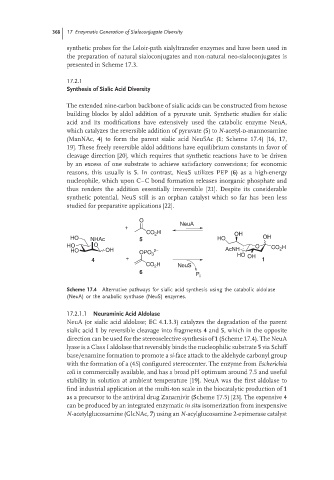
O
+ NeuA
CO 2 H OH
HO NHAc 5 HO OH
HO O O CO H
HO OH 2− AcNH 2
OPO 3 HO OH
4 + 1
CO 2 H NeuS
6
P i
Scheme 17.4 Alternative pathways for sialic acid synthesis using the catabolic aldolase
(NeuA) or the anabolic synthase (NeuS) enzymes.
17.2.1.1 Neuraminic Acid Aldolase
NeuA (or sialic acid aldolase; EC 4.1.3.3) catalyzes the degradation of the parent
sialic acid 1 by reversible cleavage into fragments 4 and 5,which in theopposite
direction can be used for the stereoselective synthesis of 1 (Scheme 17.4). The NeuA
lyase is a Class I aldolase that reversibly binds the nucleophilic substrate 5 via Schiff
base/enamine formation to promote a si-face attack to the aldehyde carbonyl group
with the formation of a (4S) configured stereocenter. The enzyme from Escherichia
coli is commercially available, and has a broad pH optimum around 7.5 and useful
stability in solution at ambient temperature [19]. NeuA was the first aldolase to
find industrial application at the multi-ton scale in the biocatalytic production of 1
as a precursor to the antiviral drug Zanamivir (Scheme 17.5) [23]. The expensive 4
can be produced by an integrated enzymatic in situ isomerization from inexpensive
N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc, 7)using an N-acylglucosamine 2-epimerase catalyst