Page 395 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 395
17.2 A Generic Strategy for the Synthesis of Sialoconjugate Libraries 371
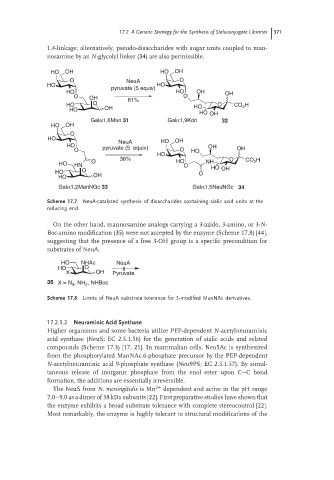
1,4-linkage; alternatively, pseudo-disaccharides with sugar units coupled to man-
nosamine by an N-glycolyl linker (34) are also permissible.
HO OH HO OH
O NeuA O
HO HO
pyruvate (5 equiv)
HO HO OH OH
O OH 81% O
HO O HO O CO H
2
HO OH
HO OH
Galα1,6Man 31 Galα1,9Kdn 32
HO OH
O
HO NeuA HO OH
HO pyruvate (5 equiv) OH
O O HO OH
HO
36% O H
HO HN O HO O NH CO 2
HO O O HO OH
HO OH
Galα1,2ManNGc 33 Galα1,5NeuNGc 34
Scheme 17.7 NeuA-catalyzed synthesis of disaccharides containing sialic acid units at the
reducing end.
On the other hand, mannosamine analogs carrying a 3-azido, 3-amino, or 3-N-
Boc-amino modification (35) were not accepted by the enzyme (Scheme 17.8) [44],
suggesting that the presence of a free 3-OH group is a specific precondition for
substrates of NeuA.
HO NHAc NeuA
HO O ll
X OH Pyruvate
35 X = N 3 , NH 2 , NHBoc
Scheme 17.8 Limits of NeuA substrate tolerance for 3-modified ManNAc derivatives.
17.2.1.2 Neuraminic Acid Synthase
Higher organisms and some bacteria utilize PEP-dependent N-acetylneuraminic
acid synthase (NeuS; EC 2.5.1.56) for the generation of sialic acids and related
compounds (Scheme 17.3) [17, 21]. In mammalian cells, Neu5Ac is synthesized
from the phosphorylated ManNAc-6-phosphate precursor by the PEP-dependent
N-acetylneuraminic acid 9-phosphate synthase (Neu9PS; EC 2.5.1.57). By simul-
taneous release of inorganic phosphate from the enol ester upon C–C bond
formation, the additions are essentially irreversible.
The NeuS from N. meningitidis is Mn 2+ dependent and active in the pH range
7.0–9.0 as a dimer of 38 kDa subunits [22]. First preparative studies have shown that
the enzyme exhibits a broad substrate tolerance with complete stereocontrol [22].
Most remarkably, the enzyme is highly tolerant to structural modifications of the