Page 396 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 396
372 17 Enzymatic Generation of Sialoconjugate Diversity
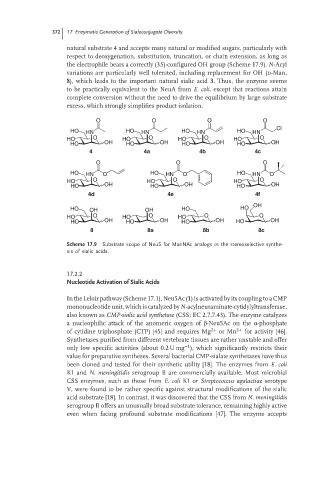
natural substrate 4 and accepts many natural or modified sugars, particularly with
respect to deoxygenation, substitution, truncation, or chain extension, as long as
the electrophile bears a correctly (3S)-configured OH group (Scheme 17.9). N-Acyl
variations are particularly well tolerated, including replacement for OH (d-Man,
8), which leads to the important natural sialic acid 3. Thus, the enzyme seems
to be practically equivalent to the NeuA from E. coli, except that reactions attain
complete conversion without the need to drive the equilibrium by large substrate
excess, which strongly simplifies product isolation.
O O O O
Cl
HO HN HO HN HO HN HO HN
HO O HO O HO O HO O
HO OH HO OH HO OH HO OH
4 4a 4b 4c
O O O
HO HN O HO HN O HO HN O
HO O HO O HO O
HO OH HO OH HO OH
4d 4e 4f
OH
HO OH OH HO HO
HO O HO O HO O O
HO OH HO OH HO OH HO OH
8 8a 8b 8c
Scheme 17.9 Substrate scope of NeuS for ManNAc analogs in the stereoselective synthe-
sis of sialic acids.
17.2.2
Nucleotide Activation of Sialic Acids
In the Leloir pathway (Scheme 17.1), Neu5Ac (1) is activated by its coupling to a CMP
mononucleotide unit, which is catalyzed by N-acylneuraminate-cytidylyltransferase,
also known as CMP-sialic acid synthetase (CSS; EC 2.7.7.43). The enzyme catalyzes
a nucleophilic attack of the anomeric oxygen of β-Neu5Ac on the α-phosphate
of cytidine triphosphate (CTP) [45] and requires Mg 2+ or Mn 2+ for activity [46].
Synthetases purified from different vertebrate tissues are rather unstable and offer
−1
only low specific activities (about 0.2 U mg ), which significantly restricts their
value for preparative syntheses. Several bacterial CMP-sialate synthetases have thus
been cloned and tested for their synthetic utility [18]. The enzymes from E. coli
K1 and N. meningitidis serogroup B are commercially available. Most microbial
CSS enzymes, such as those from E. coli K1 or Streptococcus agalactiae serotype
V, were found to be rather specific against structural modifications of the sialic
acid substrate [18]. In contrast, it was discovered that the CSS from N. meningitidis
serogroup B offers an unusually broad substrate tolerance, remaining highly active
even when facing profound substrate modifications [47]. The enzyme accepts