Page 401 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 401
17.2 A Generic Strategy for the Synthesis of Sialoconjugate Libraries 377
showed only minor improvement in substrate tolerance [42]. Clearly, a more
detailed understanding of the catalytic machinery of CSS and more elaborate cat-
alytic properties for preparative use can be expected from advanced engineering
work on this versatile enzyme scaffold.
17.2.3
Sialic Acid Transfer
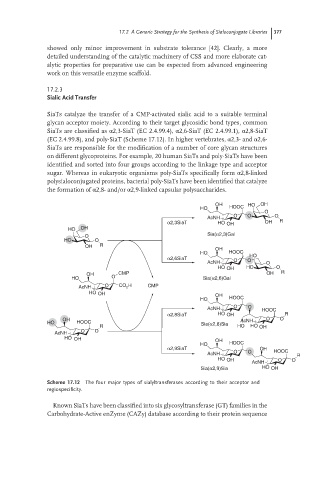
SiaTs catalyze the transfer of a CMP-activated sialic acid to a suitable terminal
glycan acceptor moiety. According to their target glycosidic bond types, common
SiaTs are classified as α2,3-SiaT (EC 2.4.99.4), α2,6-SiaT (EC 2.4.99.1), α2,8-SiaT
(EC 2.4.99.8), and poly-SiaT (Scheme 17.12). In higher vertebrates, α2,3- and α2,6-
SiaTs are responsible for the modification of a number of core glycan structures
on different glycoproteins. For example, 20 human SiaTs and poly-SiaTs have been
identified and sorted into four groups according to the linkage type and acceptor
sugar. Whereas in eukaryotic organisms poly-SiaTs specifically form α2,8-linked
polysialoconjugated proteins, bacterial poly-SiaTs have been identified that catalyze
the formation of α2,8- and/or α2,9-linked capsular polysaccharides.
OH HO OH
HO HOOC
O
O O O
AcNH
α2,3SiaT HO OH OH R
HO OH
Sia(α2,3)Gal
O
HO O
OH R
OH
HO HOOC
α2,6SiaT O O HO
AcNH O
HO OH HO O
OH CMP OH R
HO O Sia(α2,6)Gal
AcNH O CO H CMP
2
HO OH OH
HO HOOC
AcNH O O HOOC
α2,8SiaT HO OH R
OH AcNH O O
HO HOOC Sia(α2,8)Sia
R HO HO OH
AcNH O O
HO OH OH
HO HOOC
α2,9SiaT OH
AcNH O O HOOC R
HO OH O O
AcNH
Sia(α2,9)Sia HO OH
Scheme 17.12 The four major types of sialyltransferases according to their acceptor and
regiospecificity.
Known SiaTs have been classified into six glycosyltransferase (GT) families in the
Carbohydrate-Active enZyme (CAZy) database according to their protein sequence