Page 403 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 403
17.3 Cascade Synthesis of neo-Sialoconjugates 379
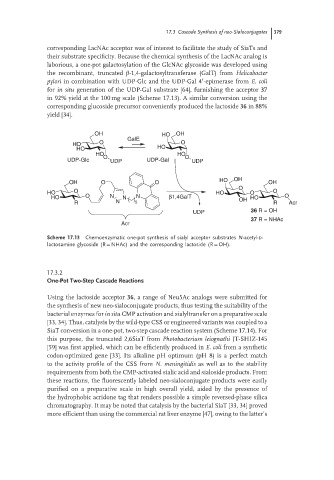
corresponding LacNAc acceptor was of interest to facilitate the study of SiaTs and
their substrate specificity. Because the chemical synthesis of the LacNAc analog is
laborious, a one-pot galactosylation of the GlcNAc glycoside was developed using
the recombinant, truncated β-1,4-galactosyltransferase (GalT) from Helicobacter
′
pylori in combination with UDP-Glc and the UDP-Gal 4 -epimerase from E. coli
for in situ generation of the UDP-Gal substrate [64], furnishing the acceptor 37
in 92% yield at the 100 mg scale (Scheme 17.13). A similar conversion using the
corresponding glucoside precursor conveniently produced the lactoside 36 in 88%
yield [34].
OH HO OH
GalE
HO O O
HO HO
HO HO
UDP-Glc O UDP UDP-Gal O UDP
OH O O HO OH OH
O
HO O HO O O
HO O N N N β1,4GalT OH HO O
R N 5 R Acr
UDP 36 R = OH
37 R = NHAc
Acr
Scheme 17.13 Chemoenzymatic one-pot synthesis of sialyl acceptor substrates N-acetyl-D-
lactosamine glycoside (R = NHAc) and the corresponding lactoside (R = OH).
17.3.2
One-Pot Two-Step Cascade Reactions
Using the lactoside acceptor 36, a range of Neu5Ac analogs were submitted for
the synthesis of new neo-sialoconjugate products, thus testing the suitability of the
bacterial enzymes for in situ CMP activation and sialyltransfer on a preparative scale
[33, 34]. Thus, catalysis by the wild-type CSS or engineered variants was coupled to a
SiaT conversion in a one-pot, two-step cascade reaction system (Scheme 17.14). For
this purpose, the truncated 2,6SiaT from Photobacterium leiognathi JT-SHIZ-145
[59] was first applied, which can be efficiently produced in E. coli from a synthetic
codon-optimized gene [33]. Its alkaline pH optimum (pH 8) is a perfect match
to the activity profile of the CSS from N. meningitidis as well as to the stability
requirements from both the CMP-activated sialic acid and sialoside products. From
these reactions, the fluorescently labeled neo-sialoconjugate products were easily
purified on a preparative scale in high overall yield, aided by the presence of
the hydrophobic acridone tag that renders possible a simple reversed-phase silica
chromatography. It may be noted that catalysis by the bacterial SiaT [33, 34] proved
more efficient than using the commercial rat liver enzyme [47], owing to the latter’s