Page 408 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 408
384 17 Enzymatic Generation of Sialoconjugate Diversity
regeneration [66]. A further benefit is that none of the synthetic intermediates
needs to be isolated and purified, thereby adding to the overall efficiency of the
procedure.
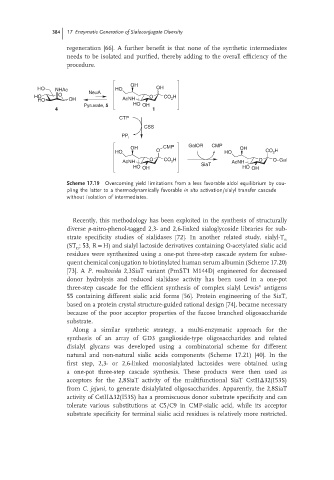
OH
HO NHAc NeuA HO OH
HO O O CO H
HO OH AcNH 2
Pyruvate, 5 HO OH
4 1
CTP
CSS
PP i
OH CMP GalOR CMP OH
HO O HO CO 2 H
O CO H O O–Gal
AcNH 2 AcNH
HO OH SiaT HO OH
Scheme 17.19 Overcoming yield limitations from a less favorable aldol equilibrium by cou-
pling the latter to a thermodynamically favorable in situ activation/sialyl transfer cascade
without isolation of intermediates.
Recently, this methodology has been exploited in the synthesis of structurally
diverse p-nitro-phenol-tagged 2,3- and 2,6-linked sialoglycoside libraries for sub-
strate specificity studies of sialidases [72]. In another related study, sialyl-T
n
(ST ; 53,R = H) and sialyl lactoside derivatives containing O-acetylated sialic acid
n
residues were synthesized using a one-pot three-step cascade system for subse-
quent chemical conjugation to biotinylated human serum albumin (Scheme 17.20)
[73]. A P. multocida 2,3SiaT variant (PmST1 M144D) engineered for decreased
donor hydrolysis and reduced sialidase activity has been used in a one-pot
x
three-step cascade for the efficient synthesis of complex sialyl Lewis antigens
55 containing different sialic acid forms [56]. Protein engineering of the SiaT,
based on a protein crystal structure-guided rational design [74], became necessary
because of the poor acceptor properties of the fucose branched oligosaccharide
substrate.
Along a similar synthetic strategy, a multi-enzymatic approach for the
synthesis of an array of GD3 ganglioside-type oligosaccharides and related
disialyl glycans was developed using a combinatorial scheme for different
natural and non-natural sialic acids components (Scheme 17.21) [40]. In the
first step, 2,3- or 2,6-linked monosialylated lactosides were obtained using
a one-pot three-step cascade synthesis. These products were then used as
acceptors for the 2,8SiaT activity of the multifunctional SiaT CstIIΔ32(I53S)
from C. jejuni, to generate disialylated oligosaccharides. Apparently, the 2,8SiaT
activity of CstIIΔ32(I53S) has a promiscuous donor substrate specificity and can
tolerate various substitutions at C5/C9 in CMP-sialic acid, while its acceptor
substrate specificity for terminal sialic acid residues is relatively more restricted.