Page 409 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 409
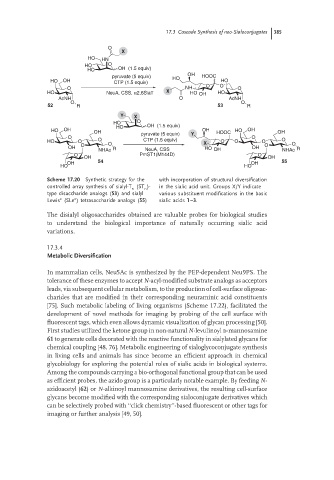
17.3 Cascade Synthesis of neo-Sialoconjugates 385
O
X
HO HN
HO O
HO OH (1.5 equiv)
OH
pyruvate (5 equiv) HO HOOC
HO OH CTP (1.5 equiv) HO
O NH O O O
HO NeuA, CSS, α2,6SiaT X HO OH HO
AcNH O AcNH
O O
52 R 53 R
Y X
HO O
HO OH (1.5 equiv)
HO OH OH pyruvate (5 equiv) Y OH HOOC HO OH OH
O O
HO O O CTP (1.5 equiv) X O O O O
O O O O
OH NHAc R NeuA, CSS HO OH OH NHAc R
O PmST1(M144D) O
OH OH
OH 54 OH 55
HO HO
Scheme 17.20 Synthetic strategy for the with incorporation of structural diversification
controlled array synthesis of sialyl-T (ST )- in the sialic acid unit. Groups X/Y indicate
n
n
type disaccharide analogs (53) and sialyl various substituent modifications in the basic
x
x
Lewis (SLe ) tetrasaccharide analogs (55) sialic acids 1–3.
The disialyl oligosaccharides obtained are valuable probes for biological studies
to understand the biological importance of naturally occurring sialic acid
variations.
17.3.4
Metabolic Diversification
In mammalian cells, Neu5Ac is synthesized by the PEP-dependent Neu9PS. The
tolerance of these enzymes to accept N-acyl-modified substrate analogs as acceptors
leads, via subsequent cellular metabolism, to the production of cell-surface oligosac-
charides that are modified in their corresponding neuraminic acid constituents
[75]. Such metabolic labeling of living organisms (Scheme 17.22), facilitated the
development of novel methods for imaging by probing of the cell surface with
fluorescent tags, which even allows dynamic visualization of glycan processing [50].
First studies utilized the ketone group in non-natural N-levulinoyl d-mannosamine
61 to generate cells decorated with the reactive functionality in sialylated glycans for
chemical coupling [48, 76]. Metabolic engineering of sialoglycoconjugate synthesis
in living cells and animals has since become an efficient approach in chemical
glycobiology for exploring the potential roles of sialic acids in biological systems.
Among the compounds carrying a bio-orthogonal functional group that can be used
as efficient probes, the azido group is a particularly notable example. By feeding N-
azidoacetyl (62)or N-alkinoyl mannosamine derivatives, the resulting cell-surface
glycans become modified with the corresponding sialoconjugate derivatives which
can be selectively probed with ‘‘click chemistry’’-based fluorescent or other tags for
imaging or further analysis [49, 50].