Page 411 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 411
17.3 Cascade Synthesis of neo-Sialoconjugates 387
O Cell Nu ∗
2
HO HN O HO OH CO H
HO O O NH O O Cell
HO OH [NeuS, PEP] HO OH
61 O
O Cell
‘‘Click’’ OH
N 3 HO CO H
2
HO HN
HO O NH O O Cell
HO OH [NeuS, PEP] N 3 HO OH
62 O
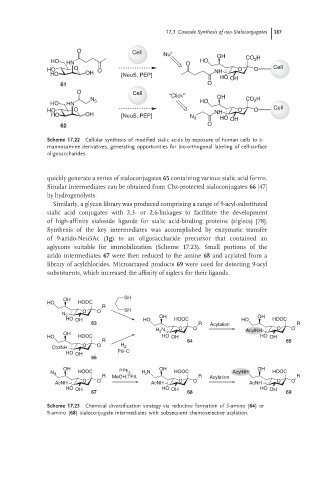
Scheme 17.22 Cellular synthesis of modified sialic acids by exposure of human cells to D-
mannosamine derivatives, generating opportunities for bio-orthogonal labeling of cell-surface
oligosaccharides.
quickly generate a series of sialoconjugates 65 containing various sialic acid forms.
Similar intermediates can be obtained from Cbz-protected sialoconjugates 66 [47]
by hydrogenolysis.
Similarly, a glycan library was produced comprising a range of 9-acyl-substituted
sialic acid conjugates with 2,3- or 2,6-linkages to facilitate the development
of high-affinity sialoside ligands for sialic acid-binding proteins (siglecs) [78].
Synthesis of the key intermediates was accomplished by enzymatic transfer
of 9-azido-Neu5Ac (1g) to an oligosaccharide precursor that contained an
aglycone suitable for immobilization (Scheme 17.23). Small portions of the
azido intermediates 67 were then reduced to the amine 68 and acylated from a
library of acylchlorides. Microarrayed products 69 were used for detecting 9-acyl
substituents, which increased the affinity of siglecs for their ligands.
OH SH
HO HOOC
R
O O SH
N 3
HO OH HO OH HOOC HO OH HOOC
63 R Acylation R
H N O O AcylNH O O
OH 2
HO HOOC HO OH HO OH
R 64 65
CbzNH O O H 2
HO OH Pd–C
66
OH OH OH
N HOOC PPh 3 H N HOOC AcylNH HOOC
3
R MeOH,TFA 2 R Acylation R
O O O O O O
AcNH AcNH AcNH
HO OH HO OH HO OH
67 68 69
Scheme 17.23 Chemical diversification strategy via reductive formation of 5-amino (64)or
9-amino (68) sialoconjugate intermediates with subsequent chemoselective acylation.