Page 390 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 390
366 17 Enzymatic Generation of Sialoconjugate Diversity
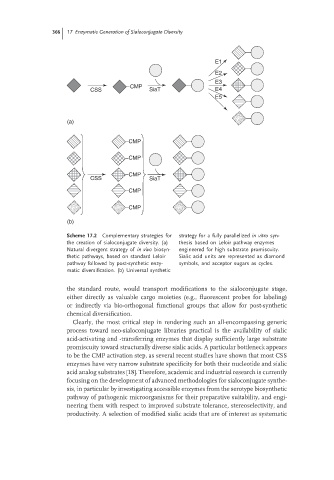
E1
E2
E3
CMP
CSS SiaT E4
E5
(a)
CMP
CMP
CMP
CSS SiaT
CMP
CMP
(b)
Scheme 17.2 Complementary strategies for strategy for a fully parallelized in vitro syn-
the creation of sialoconjugate diversity. (a) thesis based on Leloir pathway enzymes
Natural divergent strategy of in vivo biosyn- engineered for high substrate promiscuity.
thetic pathways, based on standard Leloir Sialic acid units are represented as diamond
pathway followed by post-synthetic enzy- symbols, and acceptor sugars as cycles.
matic diversification. (b) Universal synthetic
the standard route, would transport modifications to the sialoconjugate stage,
either directly as valuable cargo moieties (e.g., fluorescent probes for labeling)
or indirectly via bio-orthogonal functional groups that allow for post-synthetic
chemical diversification.
Clearly, the most critical step in rendering such an all-encompassing generic
process toward neo-sialoconjugate libraries practical is the availability of sialic
acid-activating and -transferring enzymes that display sufficiently large substrate
promiscuity toward structurally diverse sialic acids. A particular bottleneck appears
to be the CMP activation step, as several recent studies have shown that most CSS
enzymes have very narrow substrate specificity for both their nucleotide and sialic
acid analog substrates [18]. Therefore, academic and industrial research is currently
focusing on the development of advanced methodologies for sialoconjugate synthe-
sis, in particular by investigating accessible enzymes from the serotype biosynthetic
pathway of pathogenic microorganisms for their preparative suitability, and engi-
neering them with respect to improved substrate tolerance, stereoselectivity, and
productivity. A selection of modified sialic acids that are of interest as systematic