Page 425 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 425
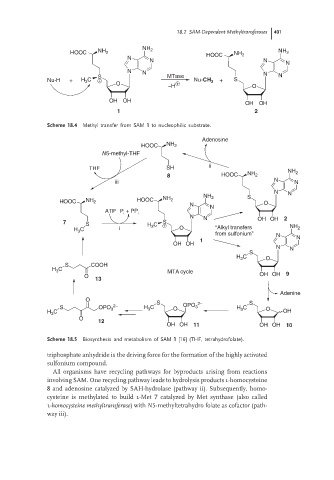
18.2 SAM-Dependent Methyltransferases 401
NH
HOOC NH 2 2 HOOC NH 2 NH 2
N
N N
N
N N
S MTase N N
Nu-H + H C Nu-CH 3 + S
3
O −H O
OH OH
OH OH
1 2
Scheme 18.4 Methyl transfer from SAM 1 to nucleophilic substrate.
Adenosine
HOOC NH 2
N5-methyl-THF
THF SH ii
NH 2
8 HOOC NH 2
N
iii N
N N
NH 2 S
HOOC NH 2 HOOC NH 2
N O
N
ATP P i + PP i
N N 2
7 S H 3 C S OH OH
H C i O “Alkyl transfers NH 2
3
from sulfonium” N
1 N
OH OH
N N
S
H 3 C O
S COOH
H 3 C
MTA cycle
O OH OH 9
13
Adenine
O S 2− S
S OPO 3 2− H C O OPO 3 H 3 C O
3
H C OH
3
O
12
OH OH 11 OH OH 10
Scheme 18.5 Biosynthesis and metabolism of SAM 1 [16] (THF, tetrahydrofolate).
triphosphate anhydride is the driving force for the formation of the highly activated
sulfonium compound.
All organisms have recycling pathways for byproducts arising from reactions
involving SAM. One recycling pathway leads to hydrolysis products l-homocysteine
8 and adenosine catalyzed by SAH-hydrolase (pathway ii). Subsequently, homo-
cysteine is methylated to build l-Met 7 catalyzed by Met synthase (also called
l-homocysteine methyltransferase)with N5-methyltetrahydro folate as cofactor (path-
way iii).