Page 426 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 426
402 18 Methyltransferases in Biocatalysis
Two families of Met synthetases have been described so far, the cobalamin-
dependent methionine synthetase (MetH) [30], and cobalamin-independent
methionine synthase (MetE) [31]. While Escherichia coli and many other prokaryotes
express both enzymes, mammals use only the cobalamin-dependent methionine
synthetase. Plants and yeasts only utilize the cobalamin-independent enzyme. In
both cases, the Met 7 derives from homocysteine 8.
The complex reactions of a second recycling pathway lead to the synthesis of Met
8 from methylthioadenosine (MTA; 9). The methylthio group of Met derives from
MTA and is not built upon methylation of homocysteine 8. This pathway is not
known in mammals [32].
The SAM synthetase is highly regulated, as an overproduction of SAM would have
dramatic impact on many cellular SAM-dependent pathways. Nevertheless, some
SAM overproducers have been constructed in the recent years [33]. Access to cheap
SAM or an efficient recycling system is the prerequisite for applications of SAM-
dependent MTs in biocatalysis and production of methylated small molecules as
active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or mediators to APIs and even high-value
specialty chemicals (for more details, see Section 18.2.4).
With purified SAM synthetase, SAM can be synthesized from l-Met 7 and ATP.
The enzymes from E. coli, yeast, and rat liver have high substrate selectivity, and
only SAM 1 can be synthesized efficiently by applying the enzymatic approach [34].
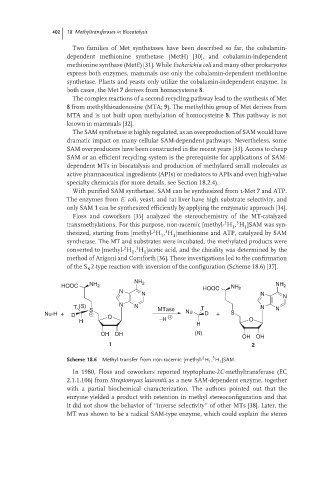
Floss and coworkers [35] analyzed the stereochemistry of the MT-catalyzed
3
2
transmethylations. For this purpose, non-racemic [methyl- H , H ]SAM was syn-
1 1
2
3
thesized, starting from [methyl- H , H ]methionine and ATP, catalyzed by SAM
1 1
synthetase. The MT and substrates were incubated, the methylated products were
2
3
converted to [methyl- H , H ]acetic acid, and the chirality was determined by the
1 1
method of Arigoni and Cornforth [36]. These investigations led to the confirmation
of the S 2-type reaction with inversion of the configuration (Scheme 18.6) [37].
N
HOOC NH 2 NH 2 HOOC NH 2 NH 2
N
N N
N
T (S) N N MTase T N N
Nu-H + D S O Nu D + S
H −H O
H
OH OH (R)
OH OH
1 2
2
3
Scheme 18.6 Methyl transfer from non-racemic [methyl- H , H ]SAM.
1
1
In 1980, Floss and coworkers reported tryptophane-2C-methyltransferase (EC
2.1.1.106) from Streptomyces laurentii as a new SAM-dependent enzyme, together
with a partial biochemical characterization. The authors pointed out that the
enzyme yielded a product with retention in methyl stereoconfiguration and that
it did not show the behavior of ‘‘inverse selectivity’’ of other MTs [38]. Later, the
MT was shown to be a radical SAM-type enzyme, which could explain the stereo