Page 83 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 83
3.1 Introduction 59
combined with a 2-hydroxybiphenyl monooxygenase (HbpA) from Pseudomonas
azaleica, which catalyzes the aromatic hydroxylation of hydroxylbiphenyl.
The concept of artificial metalloenzymes displays attractive features for both
biocatalysis and chemocatalysis: precious metal reactivity, genetic optimization
potential, and well-defined second coordination sphere provided by a protein
scaffold. Such scaffolds are further tunable by mutagenesis and can be used as
linkers for immobilization strategies.
Another example, based on the combination of heterogeneous and homogeneous
catalysis together with flow chemistry, was published by the group of Mihovilovic
[40]. (S,S)-Aerangis lactone, a natural product containing two stereogenic centers
displaying highly interesting olfactory properties, represented the target compound
of this work. This molecule was identified as the main odor component of African
white-flowering orchids and is widely used in the perfume and cosmetics industries.
A two-step strategy was envisaged, which was based on the stereoselective hydro-
genation of dihydrojasmone followed by the enzymatic Baeyer–Villiger oxidation
of the saturated ketone (Scheme 3.20).
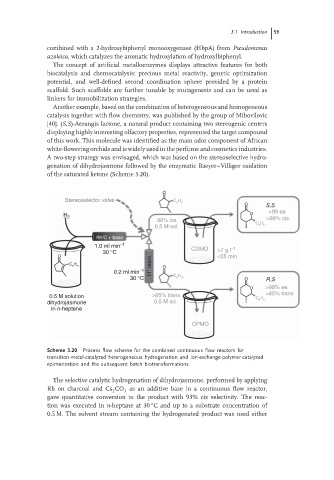
O
Stereoselector valve C H 11
5
O S,S
>99 ee
O
H 2
90% cis >99% cis
C H
0.5 M sol. 5 11
Rh/C + base
1.0 ml min −1 CDMO −1
30 °C >7 g l
O <25 min
C H
5 11 H + resin O
0.2 ml min −1
30 °C C 5 H 11 O R,S
O >99% ee
0.5 M solution >85% trans C H >85% trans
dihydrojasmone 0.5 M sol. 5 11
in n-heptene
CPMO
Scheme 3.20 Process flow scheme for the combined continuous flow reactors for
transition-metal-catalyzed heterogeneous hydrogenation and ion-exchange-polymer-catalyzed
epimerization and the subsequent batch biotransformations.
The selective catalytic hydrogenation of dihydrojasmone, performed by applying
Rh on charcoal and Cs CO as an additive base in a continuous flow reactor,
2 3
gave quantitative conversion to the product with 93% cis selectivity. The reac-
◦
tion was executed in n-heptane at 30 C and up to a substrate concentration of
0.5 M. The solvent stream containing the hydrogenated product was used either