Page 200 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 200
178 7 Electrospun Scaffolds of Biodegradable Polyesters: Manufacturing and Biomedical Application
control of the drug delivery can be extended by blending or associating polyesters
with other materials [161, 162].
Various biomolecules can be incorporated within scaffolds to enhance tis-
sue regeneration. The most frequently used biomolecules are growth factors,
cytokines, drugs, and growth factor coding genes. The controlled delivery
of these molecules by the polyester scaffolds can induce the seeded cells to
proliferate and differentiate in vitro.Meanwhile, in vivo, molecules delivered
by scaffolds may recruit cells, such as progenitor cells, toward the defect area,
thereby promoting tissue repair [163]. The electrospun scaffolds with controlled
delivery of biomolecules can be produced in a variety of ways, such as emulsion
electrospinning, coaxial electrospinning, co-electrospinning, and even blend
electrospinning. It is crucial that the integrity and the activity of the biomolecule
are preserved. The release profile is another point that needs to be observed. The
polyester should be adequately chosen to maintain a desired temporal and spatial
molecule concentration to conduct tissue regeneration. An adequate biomolecule
delivery system should release part of the dosage contained in an effective ther-
apeutic concentration and to follow with continuous release kinetics to provide
the maintenance of an adequate biomolecule concentration at the defect site.
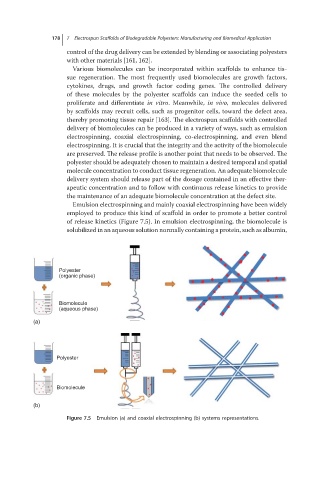
Emulsion electrospinning and mainly coaxial electrospinning have been widely
employed to produce this kind of scaffold in order to promote a better control
of release kinetics (Figure 7.5). In emulsion electrospinning, the biomolecule is
solubilized in an aqueous solution normally containing a protein, such as albumin,
Polyester
(organic phase)
Biomolecule
(aqueous phase)
(a)
Polyester
Biomolecule
(b)
Figure 7.5 Emulsion (a) and coaxial electrospinning (b) systems representations.