Page 48 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 48
26 2 Functional (Bio)degradable Polyesters by Radical Ring-Opening Polymerization
2.2
Radical Ring-Opening Polymerization (RROP) of Cyclic Ketene Acetals
2.2.1
Starting Monomers: Cyclic Ketene Acetals
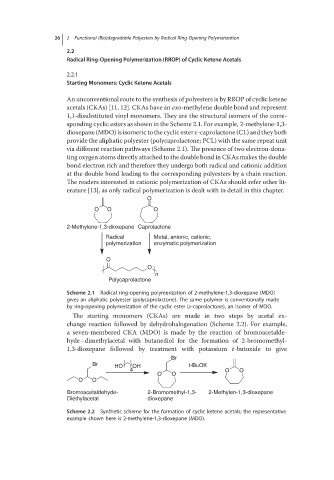
An unconventional route to the synthesis of polyesters is by RROP of cyclic ketene
acetals (CKAs) [11, 12]. CKAs have an exo-methylene double bond and represent
1,1-disubstituted vinyl monomers. They are the structural isomers of the corre-
sponding cyclic esters as shown in the Scheme 2.1. For example, 2-methylene-1,3-
dioxepane (MDO) is isomeric to the cyclic ester ε-caprolactone (CL) and they both
provide the aliphatic polyester (polycaprolactone; PCL) with the same repeat unit
via different reaction pathways (Scheme 2.1). The presence of two electron-dona-
ting oxygen atoms directly attached to the double bond in CKAs makes the double
bond electron rich and therefore they undergo both radical and cationic addition
at the double bond leading to the corresponding polyesters by a chain reaction.
The readers interested in cationic polymerization of CKAs should refer other lit-
erature [13], as only radical polymerization is dealt with in detail in this chapter.
O
O O O
2-Methylene-1,3-dioxepane Caprolactone
Radical Metal, anionic, cationic,
polymerization enzymatic polymerization
O
O
n
Polycaprolactone
Scheme 2.1 Radical ring-opening polymerization of 2-methylene-1,3-dioxepane (MDO)
gives an aliphatic polyester (polycaprolactone). The same polymer is conventionally made
by ring-opening polymerization of the cyclic ester (ε-caprolactone), an isomer of MDO.
The starting monomers (CKAs) are made in two steps by acetal ex-
change reaction followed by dehydrohalogenation (Scheme 2.2). For example,
a seven-membered CKA (MDO) is made by the reaction of bromoacetalde-
hyde–dimethylacetal with butanediol for the formation of 2-bromomethyl-
1,3-dioxepane followed by treatment with potassium t-butoxide to give
Br
Br HO OH t-BuOK
4 O O
O O
O O
Bromoacetaldehyde- 2-Bromomethyl-1,3- 2-Methylen-1,3-dioxepane
Diethylacetal dioxepane
Scheme 2.2 Synthetic scheme for the formation of cyclic ketene acetals; the representative
example shown here is 2-methylene-1,3-dioxepane (MDO).