Page 59 - Biodegradable Polyesters
P. 59
2.2 Radical Ring-Opening Polymerization (RROP) of Cyclic Ketene Acetals 37
polyesters with a range of critical temperatures for various biomedical
applications. Block copolymers of poly(NIPAAM) with polyesters such as
poly(D,L-lactide) and PCL are known. They are made in two steps: the first step
is the formation of the polyester starting from the corresponding cyclic ester
by metal-catalyzed ROP. In the second step, the OH terminal groups of the
polyesters are converted to either RAFT reagent or ATRP initiator for the con-
trolled radical polymerization of NIPAAM. [57, 58]. In the block copolymers, the
poly(NIPAAM) block would remain as it was after degradation of the polyester
part. The formation of polyesters by RROP of CKAs made it possible to bring ester
linkages randomly onto the thermoresponsive polymer backbone. The copoly-
merization of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm) and oligo(ethylene glycol)
methacrylates with BMDO using radical initiators provided degradable ther-
∘
moresponsive polymers [59, 60]. The LCST could be tuned between 31 and 67 C
with sharp phase transition for BMDO and oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate
copolymers.
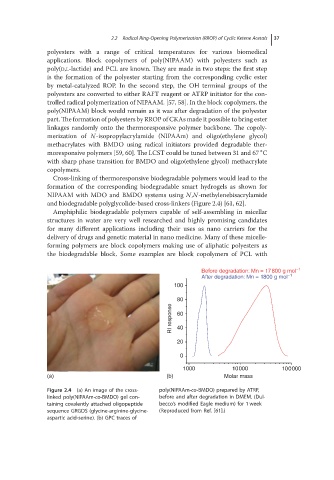
Cross-linking of thermoresponsive biodegradable polymers would lead to the
formation of the corresponding biodegradable smart hydrogels as shown for
NIPAAM with MDO and BMDO systems using N,N-methylenebisacrylamide
and biodegradable polyglycolide-based cross-linkers (Figure 2.4) [61, 62].
Amphiphilic biodegradable polymers capable of self-assembling in micellar
structures in water are very well researched and highly promising candidates
for many different applications including their uses as nano carriers for the
delivery of drugs and genetic material in nano medicine. Many of these micelle-
forming polymers are block copolymers making use of aliphatic polyesters as
the biodegradable block. Some examples are block copolymers of PCL with
Before degradation: Mn = 17 800 g mol −1
After degradation: Mn = 1800 g mol −1
100
80
RI response 60
40
20
0
1000 10 000 10 0 000
(a) (b) Molar mass
Figure 2.4 (a)Animage of thecross- poly(NIPAAm-co-BMDO) prepared by ATRP,
linked poly(NIPAAm-co-BMDO) gel con- before and after degradation in DMEM. (Dul-
taining covalently attached oligopeptide becco’s modified Eagle medium) for 1 week
sequence GRGDS (glycine-arginine-glycine- (Reproduced from Ref. [61].)
aspartic acid-serine). (b) GPC traces of