Page 241 - Biofuels Refining and Performance
P. 241
224 Chapter Eight
8.2.1 Catalytic cracking (CC)
In 1979, a paper [22] from the petrochemical industry reported for the
first time that high-molecular-weight triglycerides such as corn oil
(C H 104 O ) and castor oil (C H 104 O ) were convertible to a high-grade
57
9
57
6
gasoline when passed over H-ZSM-5, a catalyst. The latter is a synthetic,
medium-pore, shape-selective acid catalyst. Lipids were fed with a piston
displacement pump at a rate of 2 mL/h with flowing hydrogen (300 mL/h)
over 2 mL of H-ZSM-5 catalyst (0.77 g, 14–30 mesh) contained in a ver-
tical Pyrex reactor at atmospheric pressure and T 400–450 C.
Paraffins, olefins, aromatics, and nonaromatics could be detected in the
product mixture. The distribution of hydrocarbons is similar to selective
conversion of methanol into hydrocarbon units with up to 10 carbon
atoms per molecule. In all cases, a high degree of BTX aromatics (ben-
zene, toluene, and xylene) was achieved. The precondition for the catalytic
conversion is that the molecule penetrate the cavities of microporous
zeolite.
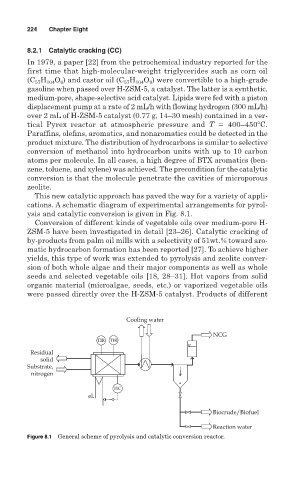
This new catalytic approach has paved the way for a variety of appli-
cations. A schematic diagram of experimental arrangements for pyrol-
ysis and catalytic conversion is given in Fig. 8.1.
Conversion of different kinds of vegetable oils over medium-pore H-
ZSM-5 have been investigated in detail [23–26]. Catalytic cracking of
by-products from palm oil mills with a selectivity of 51wt.% toward aro-
matic hydrocarbon formation has been reported [27]. To achieve higher
yields, this type of work was extended to pyrolysis and zeolite conver-
sion of both whole algae and their major components as well as whole
seeds and selected vegetable oils [18, 28–31]. Hot vapors from solid
organic material (microalgae, seeds, etc.) or vaporized vegetable oils
were passed directly over the H-ZSM-5 catalyst. Products of different
Cooling water
NCG
TIR TIR
Residual
solid
Substrate,
nitrogen
TIC
el.
Biocrude/Biofuel
Reaction water
Figure 8.1 General scheme of pyrolysis and catalytic conversion reactor.