Page 94 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 94
72 Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction
3.5.2.6 Ignition Temperature
Ignition temperature is an important property of any fuel because the com-
bustion reaction of the fuel becomes self-sustaining only above this temper-
ature. In a typical gasifier, a certain amount of combustion is necessary to
provide the energy required for drying and pyrolysis and finally for the
endothermic gasification reaction. In torrefier, temperature of cooled prod-
uct should be lower than its ignition temperature. In this context, it is
important to have some information on the ignition characteristics of
the fuel.
Exothermic chemical reactions can take place even at room temperature,
but the reaction rate, being an exponential function of temperature, is very
slow at low temperatures. The heat loss from the fuel, on the other hand, is a
linear function of temperature. At low temperatures, then, any heat released
through the reaction is lost to the surroundings at a rate faster than that at
which it was produced. As a result, the temperature of the fuel does not
increase.
When the fuel is heated by some external means, the rate of exothermic
reaction increases with a corresponding increase in the heat generation rate.
Above a certain temperature, the rate of heat generation matches or exceeds
the rate of heat loss. When this happens, the process becomes self-sustaining
and that minimum temperature is called the ignition temperature.
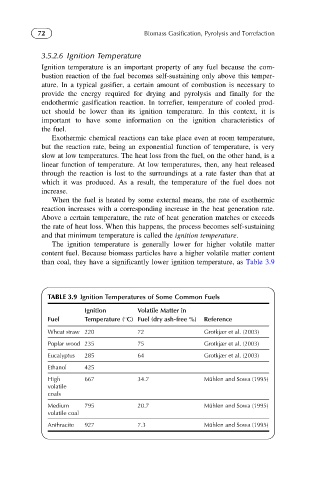
The ignition temperature is generally lower for higher volatile matter
content fuel. Because biomass particles have a higher volatile matter content
than coal, they have a significantly lower ignition temperature, as Table 3.9
TABLE 3.9 Ignition Temperatures of Some Common Fuels
Ignition Volatile Matter in
Fuel Temperature ( C) Fuel (dry ash-free %) Reference
Wheat straw 220 72 Grotkjær et al. (2003)
Poplar wood 235 75 Grotkjær et al. (2003)
Eucalyptus 285 64 Grotkjær et al. (2003)
Ethanol 425
High 667 34.7 Mu ¨hlen and Sowa (1995)
volatile
coals
Medium 795 20.7 Mu ¨hlen and Sowa (1995)
volatile coal
Anthracite 927 7.3 Mu ¨hlen and Sowa (1995)