Page 92 - Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis And Torrefaction Practical Design and Theory
P. 92
70 Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction
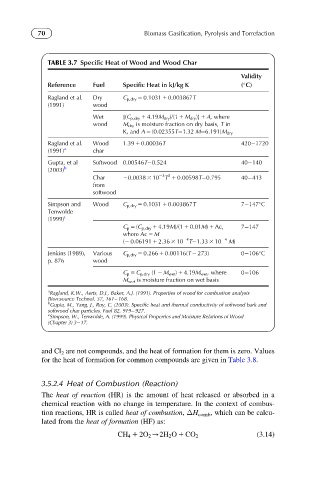
TABLE 3.7 Specific Heat of Wood and Wood Char
Validity
Reference Fuel Specific Heat in kJ/kg K ( C)
Ragland et al. Dry C p,dry 5 0.1031 1 0.003867T
(1991) wood
Wet [(C p,dry 1 4.19M dry )/(1 1 M dry )] 1 A, where
wood M dry is moisture fraction on dry basis, T in
K, and A 5 (0.02355T 1.32 M 6.191)M dry
Ragland et al. Wood 1.39 1 0.00036T 420 1720
(1991) a char
Gupta, et al Softwood 0.00546T 0.524 40 140
(2003) b
23 2
Char 20.0038 3 10 T 1 0.00598T 0.795 40 413
from
softwood
Simpson and Wood C p,dry 5 0.1031 1 0.003867T 7 147 C
Tenwolde
(1999) c
C p 5 (C p,dry 1 4.19M)/(1 1 0.01M) 1 Ac, 7 147
where Ac 5 M
24
(2 0.06191 1 2.36 3 10 T 1.33 3 10 24 M)
Jenkins (1989), Various C p,dry 5 0.266 1 0.00116(T 2 273) 0 106 C
p. 876 wood
C p 5 C p,dry (1 2 M wet ) 1 4.19M wet , where 0 106
M wet is moisture fraction on wet basis
a
Ragland, K.W., Aerts, D.J., Baker, A.J. (1991). Properties of wood for combustion analysis
Bioresource Technol. 37, 161 168.
b
Gupta, M., Yang, J., Roy, C. (2003). Specific heat and thermal conductivity of softwood bark and
softwood char particles. Fuel 82, 919 927.
c Simpson, W., Tenwolde, A. (1999). Physical Properties and Moisture Relations of Wood
(Chapter 3) 3 17.
and Cl 2 are not compounds, and the heat of formation for them is zero. Values
for the heat of formation for common compounds are given in Table 3.8.
3.5.2.4 Heat of Combustion (Reaction)
The heat of reaction (HR) is the amount of heat released or absorbed in a
chemical reaction with no change in temperature. In the context of combus-
tion reactions, HR is called heat of combustion, ΔH comb , which can be calcu-
lated from the heat of formation (HF) as:
CH 4 1 2O 2 -2H 2 O 1 CO 2 (3.14)