Page 298 - Biomedical Engineering and Design Handbook Volume 1, Fundamentals
P. 298
VIBRATION, MECHANICAL SHOCK, AND IMPACT 275
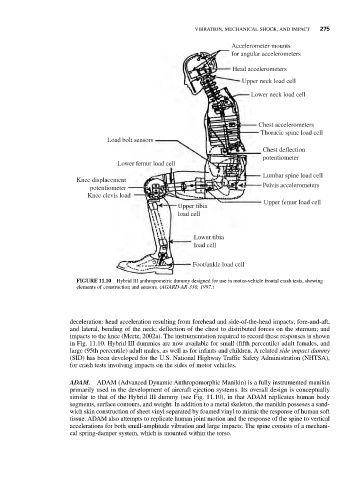
Accelerometer mounts
for angular accelerometers
Head accelerometers
Upper neck load cell
Lower neck load cell
Chest accelerometers
Thoracic spine load cell
Load bolt sensors
Chest deflection
potentiometer
Lower femur load cell
Lumbar spine load cell
Knee displacement
Pelvis accelerometers
potentiometer
Knee clevis load
Upper femur load cell
Upper tibia
load cell
Lower tibia
load cell
Foot/ankle load cell
FIGURE 11.10 Hybrid III anthropometric dummy designed for use in motor-vehicle frontal crash tests, showing
elements of construction and sensors. (AGARD-AR-330, 1997.)
deceleration: head acceleration resulting from forehead and side-of-the-head impacts; fore-and-aft,
and lateral, bending of the neck; deflection of the chest to distributed forces on the sternum; and
impacts to the knee (Mertz, 2002a). The instrumentation required to record these responses is shown
in Fig. 11.10. Hybrid III dummies are now available for small (fifth percentile) adult females, and
large (95th percentile) adult males, as well as for infants and children. A related side impact dummy
(SID) has been developed for the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA),
for crash tests involving impacts on the sides of motor vehicles.
ADAM. ADAM (Advanced Dynamic Anthropomorphic Manikin) is a fully instrumented manikin
primarily used in the development of aircraft ejection systems. Its overall design is conceptually
similar to that of the Hybrid III dummy (see Fig. 11.10), in that ADAM replicates human body
segments, surface contours, and weight. In addition to a metal skeleton, the manikin posseses a sand-
wich skin construction of sheet vinyl separated by foamed vinyl to mimic the response of human soft
tissue. ADAM also attempts to replicate human joint motion and the response of the spine to vertical
accelerations for both small-amplitude vibration and large impacts. The spine consists of a mechani-
cal spring-damper system, which is mounted within the torso.