Page 94 - Biosystems Engineering
P. 94
Biosystems Analysis and Optimization 75
Step response
1.5
Loop shaped control
P-controller
1
Amplitude
0.5
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
Time (s)
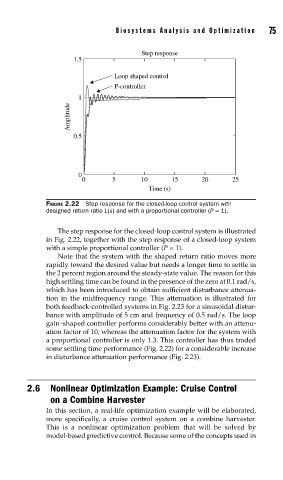
FIGURE 2.22 Step response for the closed-loop control system with
designed return ratio L(s) and with a proportional controller (P = 1).
The step response for the closed-loop control system is illustrated
in Fig. 2.22, together with the step response of a closed-loop system
with a simple proportional controller (P = 1).
Note that the system with the shaped return ratio moves more
rapidly toward the desired value but needs a longer time to settle in
the 2 percent region around the steady-state value. The reason for this
high settling time can be found in the presence of the zero at 0.1 rad/s,
which has been introduced to obtain sufficient disturbance attenua-
tion in the midfrequency range. This attenuation is illustrated for
both feedback-controlled systems in Fig. 2.23 for a sinusoidal distur-
bance with amplitude of 5 cm and frequency of 0.5 rad/s. The loop
gain–shaped controller performs considerably better with an attenu-
ation factor of 10, whereas the attenuation factor for the system with
a proportional controller is only 1.3. This controller has thus traded
some settling time performance (Fig. 2.22) for a considerable increase
in disturbance attenuation performance (Fig. 2.23).
2.6 Nonlinear Optimization Example: Cruise Control
on a Combine Harvester
In this section, a real-life optimization example will be elaborated,
more specifically, a cruise control system on a combine harvester.
This is a nonlinear optimization problem that will be solved by
model-based predictive control. Because some of the concepts used in