Page 173 - Bridge and Highway Structure Rehabilitation and Repair
P. 173
148 SECTION 2 STRENGTHENING AND REPAIR WORK
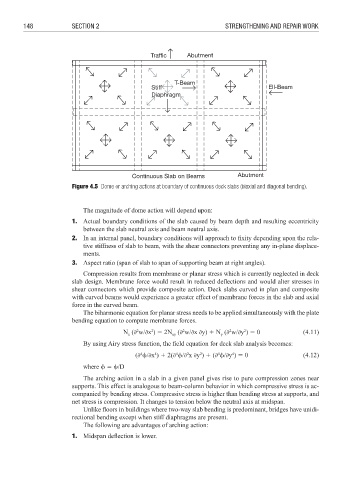
Traffic Abutment
T-Beam
Stiff Ell-Beam
Diaphragm
Continuous Slab on Beams Abutment
Figure 4.5 Dome or arching actions at boundary of continuous deck slabs (biaxial and diagonal bending).
The magnitude of dome action will depend upon:
1. Actual boundary conditions of the slab caused by beam depth and resulting eccentricity
between the slab neutral axis and beam neutral axis.
2. In an internal panel, boundary conditions will approach to fixity depending upon the rela-
tive stiffness of slab to beam, with the shear connectors preventing any in-plane displace-
ments.
3. Aspect ratio (span of slab to span of supporting beam at right angles).
Compression results from membrane or planar stress which is currently neglected in deck
slab design. Membrane force would result in reduced deflections and would alter stresses in
shear connectors which provide composite action. Deck slabs curved in plan and composite
with curved beams would experience a greater effect of membrane forces in the slab and axial
force in the curved beam.
The biharmonic equation for planar stress needs to be applied simultaneously with the plate
bending equation to compute membrane forces.
2
2
2
2
2
N (; w/;x ) 6 2N (; w/;x ;y) 4 N (; w/;y ) 3 0 (4.11)
xy
y
x
By using Airy stress function, the field equation for deck slab analysis becomes:
2
2
4
4
4
4
4
(; )/;x ) 4 2(; )/; x ;y ) 4 (; )/;y ) 3 0 (4.12)
where ) 3 -/D
The arching action in a slab in a given panel gives rise to pure compression zones near
supports. This effect is analogous to beam-column behavior in which compressive stress is ac-
companied by bending stress. Compressive stress is higher than bending stress at supports, and
net stress is compression. It changes to tension below the neutral axis at midspan.
Unlike floors in buildings where two-way slab bending is predominant, bridges have unidi-
rectional bending except when stiff diaphragms are present.
The following are advantages of arching action:
1. Midspan deflection is lower.