Page 245 - Build Your Own Transistor Radios a Hobbyists Guide to High-Performance and Low-Powered Radio Circuits
P. 245
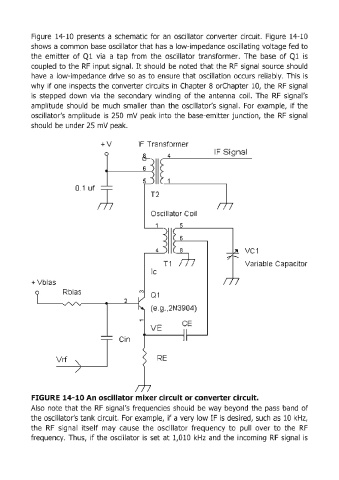
Figure 14-10 presents a schematic for an oscillator converter circuit. Figure 14-10
shows a common base oscillator that has a low-impedance oscillating voltage fed to
the emitter of Ql via a tap from the oscillator transformer. The base of Q1 is
coupled to the RF input signal. It should be noted that the RF signal source should
have a low-impedance drive so as to ensure that oscillation occurs reliably. This is
why if one inspects the converter circuits in Chapter 8 orChapter 10, the RF signal
is stepped down via the secondary winding of the antenna coil. The RF signal's
amplitude should be much smaller than the oscillator's signal. For example, if the
oscillator's amplitude is 250 mV peak into the base-emitter junction, the RF signal
should be under 25 mV peak.
IF Signal
VC1
Variable Capacitor
FIGURE 14-10 An oscillator mixer circuit or converter circuit.
Also note that the RF signal's frequencies should be way beyond the pass band of
the oscillator's tank circuit. For example, if a very low IF is desired, such as 10 kHz,
the RF signal itself may cause the oscillator frequency to pullover to the RF
frequency. Thus, if the oscillator is set at 1,OlD kHz and the incoming RF signal is