Page 130 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 130
122 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
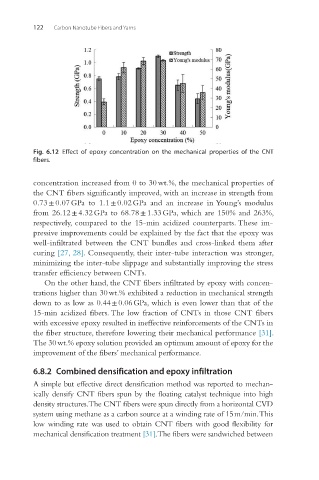
Fig. 6.12 Effect of epoxy concentration on the mechanical properties of the CNT
fibers.
concentration increased from 0 to 30 wt.%, the mechanical properties of
the CNT fibers significantly improved, with an increase in strength from
0.73 ± 0.07 GPa to 1.1 ± 0.02 GPa and an increase in Young’s modulus
from 26.12 ± 4.32 GPa to 68.78 ± 1.33 GPa, which are 150% and 263%,
respectively, compared to the 15-min acidized counterparts. These im-
pressive improvements could be explained by the fact that the epoxy was
well-infiltrated between the CNT bundles and cross-linked them after
curing [27, 28]. Consequently, their inter-tube interaction was stronger,
minimizing the inter-tube slippage and substantially improving the stress
transfer efficiency between CNTs.
On the other hand, the CNT fibers infiltrated by epoxy with concen-
trations higher than 30 wt.% exhibited a reduction in mechanical strength
down to as low as 0.44 ± 0.06 GPa, which is even lower than that of the
15-min acidized fibers. The low fraction of CNTs in those CNT fibers
with excessive epoxy resulted in ineffective reinforcements of the CNTs in
the fiber structure, therefore lowering their mechanical performance [31].
The 30 wt.% epoxy solution provided an optimum amount of epoxy for the
improvement of the fibers’ mechanical performance.
6.8.2 Combined densification and epoxy infiltration
A simple but effective direct densification method was reported to mechan-
ically densify CNT fibers spun by the floating catalyst technique into high
density structures. The CNT fibers were spun directly from a horizontal CVD
system using methane as a carbon source at a winding rate of 15 m/min. This
low winding rate was used to obtain CNT fibers with good flexibility for
mechanical densification treatment [31]. The fibers were sandwiched between