Page 135 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 135
80
Strength
70 Young’s modulus
Improvement factor 50
60
40
30
20
10
0
liquid acid laser liquid Mechanical Mechanical
densification treatment treatment densification densification densification
+ infiltration + infiltration
(A) Post-treatment methods
6 CNT ribbon from
aerogel spinning
5
Tensile strength (GPa) 4 3 CNT fiber from PAN carbon fiber
array spinning
wet spinning
CNT fiber
1 2 CNT fiber from This work
CNT ribbon
Cross-linked CNT ribbon
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
(B) Young’s modulus (GPa)
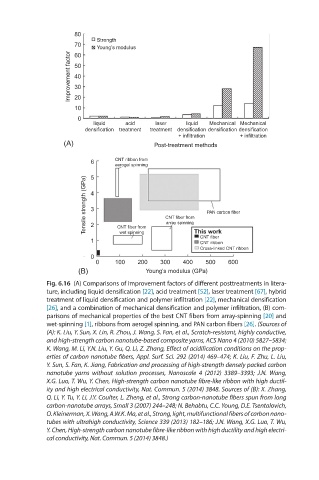
Fig. 6.16 (A) Comparisons of improvement factors of different posttreatments in litera-
ture, including liquid densification [22], acid treatment [52], laser treatment [67], hybrid
treatment of liquid densification and polymer infiltration [22], mechanical densification
[26], and a combination of mechanical densification and polymer infiltration, (B) com-
parisons of mechanical properties of the best CNT fibers from array-spinning [20] and
wet-spinning [1], ribbons from aerogel spinning, and PAN carbon fibers [26]. (Sources of
(A): K. Liu, Y. Sun, X. Lin, R. Zhou, J. Wang, S. Fan, et al., Scratch-resistant, highly conductive,
and high-strength carbon nanotube-based composite yarns, ACS Nano 4 (2010) 5827–5834;
K. Wang, M. Li, Y.N. Liu, Y. Gu, Q. Li, Z. Zhang, Effect of acidification conditions on the prop-
erties of carbon nanotube fibers, Appl. Surf. Sci. 292 (2014) 469–474; K. Liu, F. Zhu, L. Liu,
Y. Sun, S. Fan, K. Jiang, Fabrication and processing of high-strength densely packed carbon
nanotube yarns without solution processes, Nanoscale 4 (2012) 3389–3393; J.N. Wang,
X.G. Luo, T. Wu, Y. Chen, High-strength carbon nanotube fibre-like ribbon with high ductil-
ity and high electrical conductivity, Nat. Commun. 5 (2014) 3848. Sources of (B): X. Zhang,
Q. Li, Y. Tu, Y. Li, J.Y. Coulter, L. Zheng, et al., Strong carbon-nanotube fibers spun from long
carbon-nanotube arrays, Small 3 (2007) 244–248; N. Behabtu, C.C. Young, D.E. Tsentalovich,
O. Kleinerman, X. Wang, A.W.K. Ma, et al., Strong, light, multifunctional fibers of carbon nano-
tubes with ultrahigh conductivity, Science 339 (2013) 182–186; J.N. Wang, X.G. Luo, T. Wu,
Y. Chen, High-strength carbon nanotube fibre-like ribbon with high ductility and high electri-
cal conductivity, Nat. Commun. 5 (2014) 3848.)