Page 136 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 136
128 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
[22], acid treatment [52], laser treatment [67], hybrid treatment of liquid den-
sification and polymer infiltration [22], and mechanical densification [26]. The
hybrid posttreatment is the most effective method, with improvement factors
of more than 13.5 for tensile strength and 63 for Young’s modulus.
The strength and Young’s modulus of the CNT ribbons and epoxy-
infiltrated CNT ribbons are much higher than those of the CNT fibers post-
treated by the other methods. As shown in Fig. 6.16B, the tensile strength
of the densified CNT ribbons is higher than that of the best CNT fibers
spun from wet-spinning and array-spinning methods. After further infil-
trated with the epoxy, the CNT composite ribbons reach a high strength of
up to 5.2 GPa and Young’s modulus of up to 444 GPa, which are comparable
to those of commercial PAN carbon fibers. Moreover, the strength of the
CNT-epoxy composite ribbons is comparable to that of the best DWNT
ribbons fabricated by the floating catalyst method (5.53 GPa) [26] but with
much higher Young’s modulus.
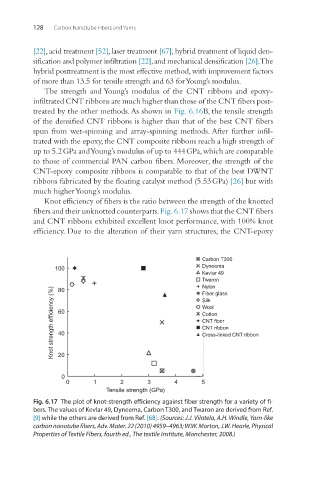
Knot efficiency of fibers is the ratio between the strength of the knotted
fibers and their unknotted counterparts. Fig. 6.17 shows that the CNT fibers
and CNT ribbons exhibited excellent knot performance, with 100% knot
efficiency. Due to the alteration of their yarn structures, the CNT-epoxy
Carbon T300
100 Dyneema
Kevlar 49
Twaron
Nylon
80
Knot strength efficiency (%) 60 Wool
Fiber glass
Silk
Cotton
CNT fiber
CNT ribbon
40
Cross-linked CNT ribbon
20
0
0 1 2 3 4 5
Tensile strength (GPa)
Fig. 6.17 The plot of knot-strength efficiency against fiber strength for a variety of fi-
bers. The values of Kevlar 49, Dyneema, Carbon T300, and Twaron are derived from Ref.
[9] while the others are derived from Ref. [68]. (Sources: J.J. Vilatela, A.H. Windle, Yarn-like
carbon nanotube fibers, Adv. Mater. 22 (2010) 4959–4963; W.W. Morton, J.W. Hearle, Physical
Properties of Textile Fibers, fourth ed., The textile Institute, Manchester, 2008.)