Page 51 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 51
44 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
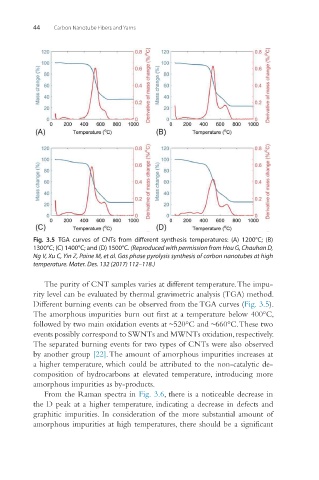
Fig. 3.5 TGA curves of CNTs from different synthesis temperatures: (A) 1200°C; (B)
1300°C; (C) 1400°C; and (D) 1500°C. (Reproduced with permission from Hou G, Chauhan D,
Ng V, Xu C, Yin Z, Paine M, et al. Gas phase pyrolysis synthesis of carbon nanotubes at high
temperature. Mater. Des. 132 (2017) 112–118.)
The purity of CNT samples varies at different temperature. The impu-
rity level can be evaluated by thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) method.
Different burning events can be observed from the TGA curves (Fig. 3.5).
The amorphous impurities burn out first at a temperature below 400°C,
followed by two main oxidation events at ~520°C and ~660°C. These two
events possibly correspond to SWNTs and MWNTs oxidation, respectively.
The separated burning events for two types of CNTs were also observed
by another group [22]. The amount of amorphous impurities increases at
a higher temperature, which could be attributed to the non-catalytic de-
composition of hydrocarbons at elevated temperature, introducing more
amorphous impurities as by-products.
From the Raman spectra in Fig. 3.6, there is a noticeable decrease in
the D peak at a higher temperature, indicating a decrease in defects and
graphitic impurities. In consideration of the more substantial amount of
amorphous impurities at high temperatures, there should be a significant