Page 225 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 225
188 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
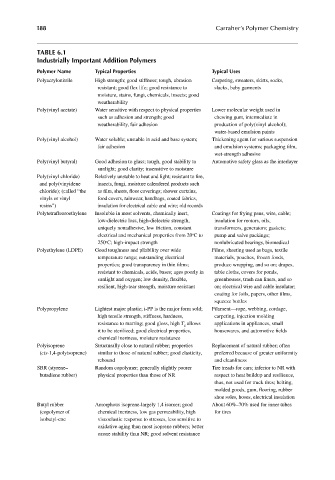
TABLE 6.1
Industrially Important Addition Polymers
Polymer Name Typical Properties Typical Uses
Polyacrylonitrile High strength; good stiffness; tough, abrasion Carpeting, sweaters, skirts, socks,
resistant; good flex life; good resistance to slacks, baby garments
moisture, stains, fungi, chemicals, insects; good
weatherability
Poly(vinyl acetate) Water sensitive with respect to physical properties Lower molecular weight used in
such as adhesion and strength; good chewing gum, intermediate in
weatherability, fair adhesion production of poly(vinyl alcohol);
water-based emulsion paints
Poly(vinyl alcohol) Water soluble; unstable in acid and base system; Thickening agent for various suspension
fair adhesion and emulsion systems; packaging fi lm,
wet-strength adhesive
Poly(vinyl butyral) Good adhesion to glass; tough, good stability to Automotive safety glass as the interlayer
sunlight; good clarity; insensitive to moisture
Poly(vinyl chloride) Relatively unstable to heat and light; resistant to fi re,
and poly(vinyidene insects, fungi, moisture calendered products such
chloride); (called “the as film, sheets, floor coverings; shower curtains,
vinyls or vinyl food covers, rainwear, handbags, coated fabrics,
resins”) insulation for electrical cable and wire; old records
Polytetrafluoroethylene Insoluble in most solvents, chemically inert, Coatings for frying pans, wire, cable;
low-dielectric loss, high-dielectric strength, insulation for motors, oils,
uniquely nonadhesive, low friction, constant transformers, generators; gaskets;
o
electrical and mechanical properties from 20 C to pump and valve packings;
o
250 C; high-impact strength nonlubricated bearings, biomedical
Polyethylene (LDPE) Good toughness and pliability over wide Films, sheeting used as bags, textile
temperature range; outstanding electrical materials, pouches, frozen foods,
properties; good transparency in thin fi lms; produce wrapping, and so on; drapes,
resistant to chemicals, acids, bases; ages poorly in table cloths, covers for ponds,
sunlight and oxygen; low density, fl exible, greenhouses, trash can liners, and so
resilient, high-tear strength, moisture resistant on; electrical wire and cable insulator;
coating for foils, papers, other fi lms,
squeeze bottles
Polypropylene Lightest major plastic; i-PP is the major form sold; Filament—rope, webbing, cordage,
high tensile strength, stiffness, hardness, carpeting, injection molding
resistance to marring; good gloss, high T g allows applications in appliances, small
it to be sterilized; good electrical properties, housewares, and automotive fi elds
chemical inertness, moisture resistance
Polyisoprene Structurally close to natural rubber; properties Replacement of natural rubber; often
(cis-1,4-polyisoprene) similar to those of natural rubber; good elasticity, preferred because of greater uniformity
rebound and cleanliness
SBR (styrene– Random copolymer; generally slightly poorer Tire treads for cars; inferior to NR with
butadiene rubber) physical properties than those of NR respect to heat buildup and resilience,
thus, not used for truck tires; belting,
molded goods, gum, fl ooring, rubber
shoe soles, hoses, electrical insulation
Butyl rubber Amorphous isoprene-largely 1,4 isomer; good About 60%–70% used for inner tubes
(copolymer of chemical inertness, low gas permeability, high for tires
isobutyl-ene viscoelastic response to stresses, less sensitive to
oxidative aging than most isoprene rubbers; better
ozone stability than NR; good solvent resistance
9/14/2010 3:39:21 PM
K10478.indb 188
K10478.indb 188 9/14/2010 3:39:21 PM